Complications associated with ureterorenoscopy (URS) related to treatment of urolithiasis: the Clinical Research Office of Endourological Society URS Global study
- PMID: 27492012
- PMCID: PMC5364249
- DOI: 10.1007/s00345-016-1909-0
Complications associated with ureterorenoscopy (URS) related to treatment of urolithiasis: the Clinical Research Office of Endourological Society URS Global study
Abstract
Introduction: Ureterorenoscopy (URS) is a popular and growing option for management of ureteric and renal stones. The CROES URS Global Study was set up to assess the outcomes of URS in a large worldwide cohort of patients involving multiple centres. In this paper, we analysed the database for intra-operative and post-operative complications associated with ureterorenoscopy.
Methods: The CROES database was established via collaboration between 114 centres in 32 countries worldwide, and information on both intra-operative and post-operative complications was collected electronically between January 2010 and October 2012.
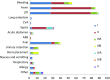
Result: On analysis of a total of 11,885 patients, the overall complication and stone-free rates were found to be 7.4 and 85.6 %, respectively. The intra-operative and post-operative complication rates were 4.2 and 2.6 %, respectively, and in total 5 deaths were reported in the study period. Taking into account different world economies, there were no differences in the complication rates between the developing and developed nations or between different centres from different continents.
Conclusion: Ureterorenoscopy is a safe and effective procedure for treatment of stones, the outcomes of which are broadly comparable in different parts of the world for similar patient and stone demographics.
Keywords: Clavien–Dindo; Complications; Ureterorenoscopy; Urolithiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
No competing financial interests exist.
Ethical standard
All human studies have been approved by the appropriate ethics committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical