Long-range movement of large mechanically interlocked DNA nanostructures
- PMID: 27492061
- PMCID: PMC4980458
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12414
Long-range movement of large mechanically interlocked DNA nanostructures
Abstract
Interlocked molecules such as catenanes and rotaxanes, connected only via mechanical bonds have the ability to perform large-scale sliding and rotational movements, making them attractive components for the construction of artificial molecular machines and motors. We here demonstrate the realization of large, rigid rotaxane structures composed of DNA origami subunits. The structures can be easily modified to carry a molecular cargo or nanoparticles. By using multiple axle modules, rotaxane constructs are realized with axle lengths of up to 355 nm and a fuel/anti-fuel mechanism is employed to switch the rotaxanes between a mobile and a fixed state. We also create extended pseudo-rotaxanes, in which origami rings can slide along supramolecular DNA filaments over several hundreds of nanometres. The rings can be actively moved and tracked using atomic force microscopy.
Figures
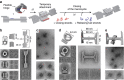
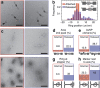
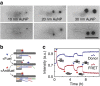
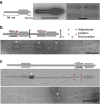
References
-
- Ashton P. R. et al.. A [2]Catenane made to order. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 28, 1396–1399 (1989).
-
- Amabilino D. B. & Stoddart J. F. Interlocked and intertwined structures and superstructures. Chem. Rev. 95, 2725–2828 (1995).
-
- Balzani V., Credi A. & Venturi M. Molecular Devices and Machines Wiley-VCH (2003).
-
- Kay E. R., Leigh D. A. & Zerbetto F. Synthetic molecular motors and mechanical machines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 46, 72–191 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Badjic J. D., Balzani V., Credi A., Silvi S. & Stoddart J. F. A molecular elevator. Science 303, 1845–1849 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

