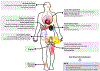
Ten tips for managing critically ill patients with sickle cell disease
- PMID: 27492270
- PMCID: PMC7194474
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-016-4472-7
Ten tips for managing critically ill patients with sickle cell disease
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cecchini J, Lionnet F, Djibré M et al. (2014) Outcomes of adult patients with sickle cell disease admitted to the ICU: a case series. Crit Care Med 42:1629–1639 - PubMed
-
- Mekontso Dessap A, Deux J, Abidi N et al. (2011) Pulmonary artery thrombosis during acute chest syndrome in sickle cell disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 184:1022–1029 - PubMed
-
- Vichinsky EP, Neumayr LD, Earles AN et al. (2000) Causes and outcomes of the acute chest syndrome in sickle cell disease. National Acute Chest Syndrome Study Group. N Engl J Med 342:1855–1865 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

