PTEN regulates EG5 to control spindle architecture and chromosome congression during mitosis
- PMID: 27492783
- PMCID: PMC4980451
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12355
PTEN regulates EG5 to control spindle architecture and chromosome congression during mitosis
Abstract
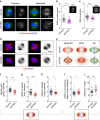
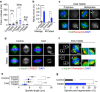
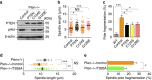
Architectural integrity of the mitotic spindle is required for efficient chromosome congression and accurate chromosome segregation to ensure mitotic fidelity. Tumour suppressor PTEN has multiple functions in maintaining genome stability. Here we report an essential role of PTEN in mitosis through regulation of the mitotic kinesin motor EG5 for proper spindle architecture and chromosome congression. PTEN depletion results in chromosome misalignment in metaphase, often leading to catastrophic mitotic failure. In addition, metaphase cells lacking PTEN exhibit defects of spindle geometry, manifested prominently by shorter spindles. PTEN is associated and co-localized with EG5 during mitosis. PTEN deficiency induces aberrant EG5 phosphorylation and abrogates EG5 recruitment to the mitotic spindle apparatus, leading to spindle disorganization. These data demonstrate the functional interplay between PTEN and EG5 in controlling mitotic spindle structure and chromosome behaviour during mitosis. We propose that PTEN functions to equilibrate mitotic phosphorylation for proper spindle formation and faithful genomic transmission.
Figures
References
-
- Yin Y. & Shen W. H. PTEN: a new guardian of the genome. Oncogene 27, 5443–5453 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Puc J. et al.. Lack of PTEN sequesters CHK1 and initiates genetic instability. Cancer Cell 7, 193–204 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Shen W. H. et al.. Essential role for nuclear PTEN in maintaining chromosomal integrity. Cell 128, 157–170 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

