Overexpression of angiopoietin 2 promotes the formation of oral squamous cell carcinoma by increasing epithelial-mesenchymal transition-induced angiogenesis
- PMID: 27492854
- PMCID: PMC5033983
- DOI: 10.1038/cgt.2016.30
Overexpression of angiopoietin 2 promotes the formation of oral squamous cell carcinoma by increasing epithelial-mesenchymal transition-induced angiogenesis
Abstract
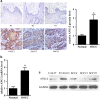
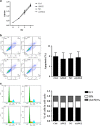
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the most common cancer of the head and neck and is associated with a high rate of lymph node metastasis. The initial step in the metastasis and transition of tumors is epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-induced angiogenesis, which can be mediated by angiopoietin 2 (ANG2), a key regulatory factor in angiogenesis. In the present study, immunohistochemistry and real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase (qRT-PCR) were used to measure the expression of ANG2 in OSCC tissues. Plasmids encoding ANG2 mRNA were used for increased ANG2 expression in the OSCC cell line TCA8113. The short interfering RNA (siRNA)-targeting ANG2 mRNA sequences were used to inhibit ANG2 expression in TCA8113 cells. Subsequently, transwell assays were performed to examine the effects of ANG2 on TCA8113 cell migration and invasion. Furthermore, in vivo assays were performed to assess the effect of ANG2 on tumor growth. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assays and immunohistochemistry were used to examine cell apoptosis and angiogenesis in tumor tissues, respectively. Finally, western blot analysis was performed to evaluate tumor formation-related proteins in OSCC tissues. We found that protein expression of ANG2 was remarkably upregulated in OSCC tissues. Overexpression of ANG2 increased the migration and invasion of TCA8113 cells by regulating EMT. Further investigations showed that overexpression of ANG2 increased tumor growth in nude mice, and angiogenesis of OSCC tissues increased in the presence of ANG2 overexpression. Overexpression of ANG2 also reduced cell apoptosis in tumor tissue cells. Finally, we found that overexpression of ANG2 resulted in changes in the expression of tumor formation-related proteins including vimentin, E-cadherin, Bim, PUMA, Bcl-2, Bax, Cyclin D1, PCNA and CD31. Our findings show that ANG2 has an important role in the migration and invasion of OSCC. More importantly, further investigations suggested that overexpression of ANG2 might increase OSCC metastasis by promoting angiogenesis in nude mice. This stimulatory effect could be achieved by inducing abnormal EMT and by reducing apoptosis and increasing proliferation of cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Angiogenic Factors on the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Their Impact on the Onset and Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview.Cells. 2024 Jul 31;13(15):1294. doi: 10.3390/cells13151294. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-146a promotes proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous carcinoma cells.Environ Toxicol. 2020 Oct;35(10):1050-1057. doi: 10.1002/tox.22941. Epub 2020 May 29. Environ Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32469461
-
Long Non Coding RNA MALAT1 Promotes Tumor Growth and Metastasis by inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 2;5:15972. doi: 10.1038/srep15972. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26522444 Free PMC article.
-
MUC1 gene silencing inhibits proliferation, invasion, and migration while promoting apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.Biosci Rep. 2019 Sep 16;39(9):BSR20182193. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182193. Print 2019 Sep 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. Retraction in: Biosci Rep. 2020 Aug 28;40(8):BSR-20182193_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-20182193_RET. PMID: 31439759 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Challenges and opportunities.Int J Cancer. 2021 Apr 1;148(7):1548-1561. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33352. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Int J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33091960 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Angiogenic Factors on the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Their Impact on the Onset and Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview.Cells. 2024 Jul 31;13(15):1294. doi: 10.3390/cells13151294. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic co-culture of pancreatic tumor spheroids with stellate cells as a novel 3D model for investigation of stroma-mediated cell motility and drug resistance.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jan 12;37(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0654-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29329547 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-dependent angiopoietin-Tie2 and nitric oxide signaling of erythrocytes in response to surgical trauma in head and neck cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Aug 16;18(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01991-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32799882 Free PMC article.
-
Doxorubicin-loaded PEGylated liposome modified with ANGPT2-specific peptide for integrative glioma-targeted imaging and therapy.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jan 4;30:101455. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101455. eCollection 2025 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 39866777 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker Potential of Vimentin in Oral Cancers.Life (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;12(2):150. doi: 10.3390/life12020150. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

