Agonist-induced internalization and desensitization of the apelin receptor
- PMID: 27492965
- PMCID: PMC5062952
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.07.040
Agonist-induced internalization and desensitization of the apelin receptor
Abstract
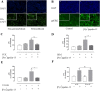
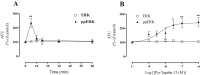
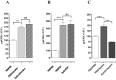
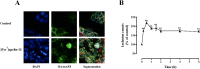
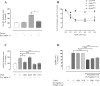
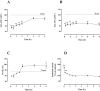
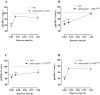
Apelin acts via the G protein-coupled apelin receptor (APJ) to mediate effects on cardiovascular and fluid homeostasis. G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) trafficking has an important role in the regulation of receptor signalling pathways and cellular functions, however in the case of APJ the mechanisms and proteins involved in apelin-induced trafficking are not well understood. We generated a stable HEK-293 cell line expressing N-terminus HA-tagged mouse (m) APJ, and used a semi-automated imaging protocol to quantitate APJ trafficking and ERK1/2 activation following stimulation with [Pyr1]apelin-13. The mechanisms of [Pyr1]apelin-13-induced internalization and desensitization were explored using dominant-negative mutant (DNM) cDNA constructs of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2), β-arrestin1, EPS15 and dynamin. The di-phosphorylated ERK1/2 (ppERK1/2) response to [Pyr1]apelin-13 desensitized during sustained stimulation, due to upstream APJ-specific adaptive changes. Furthermore, [Pyr1]apelin-13 stimulation caused internalization of mAPJ via clathrin coated vesicles (CCVs) and also caused a rapid reduction in cell surface and whole cell HA-mAPJ. Our data suggest that upon continuous agonist exposure GRK2-mediated phosphorylation targets APJ to CCVs that are internalized from the cell surface in a β-arrestin1-independent, EPS15- and dynamin-dependent manner. Internalization does not appear to contribute to the desensitization of APJ-mediated ppERK1/2 activation in these cells.
Keywords: Apelin; Apelin receptor; Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK); G protein-coupled receptor; Intracellular trafficking; Signalling.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn S., Shenoy S.K., Wei H., Lefkowitz R.J. Differential kinetic and spatial patterns of beta-arrestin and G protein-mediated ERK activation by the angiotensin II receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:35518–35525. - PubMed
-
- Bai B., Tang J., Liu H., Chen J., Li Y., Song W. Apelin-13 induces ERK1/2 but not p38 MAPK activation through coupling of the human apelin receptor to the Gi2 pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 2008;40:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Benovic J.L., Pike L.J., Cerione R.A., Staniszewski C., Yoshimasa T., Codina J., Caron M.G., Lefkowitz R.J. Phosphorylation of the mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor by cyclic AMP dependent protein kinase. Regulation of the rate of receptor phosphorylation and dephosphorylation by agonist occupancy and effects on coupling of the receptor to the stimulatory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:7094–7101. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar A., Willins D.L., Gray J.A., Woods J., Benovic J.L., Roth B.L. The dynamin-dependent, arrestin-independent internalization of 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A (5-HT2A) serotonin receptors reveals differential sorting of arrestins and 5-HT2A receptors during endocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:8269–8277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

