Value of Donor-Specific Anti-HLA Antibody Monitoring and Characterization for Risk Stratification of Kidney Allograft Loss
- PMID: 27493255
- PMCID: PMC5280026
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2016030368
Value of Donor-Specific Anti-HLA Antibody Monitoring and Characterization for Risk Stratification of Kidney Allograft Loss
Abstract
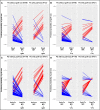
The diagnosis system for allograft loss lacks accurate individual risk stratification on the basis of donor-specific anti-HLA antibody (anti-HLA DSA) characterization. We investigated whether systematic monitoring of DSA with extensive characterization increases performance in predicting kidney allograft loss. This prospective study included 851 kidney recipients transplanted between 2008 and 2010 who were systematically screened for DSA at transplant, 1 and 2 years post-transplant, and the time of post-transplant clinical events. We assessed DSA characteristics and performed systematic allograft biopsies at the time of post-transplant serum evaluation. At transplant, 110 (12.9%) patients had DSAs; post-transplant screening identified 186 (21.9%) DSA-positive patients. Post-transplant DSA monitoring improved the prediction of allograft loss when added to a model that included traditional determinants of allograft loss (increase in c statistic from 0.67; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.62 to 0.73 to 0.72; 95% CI, 0.67 to 0.77). Addition of DSA IgG3 positivity or C1q binding capacity increased discrimination performance of the traditional model at transplant and post-transplant. Compared with DSA mean fluorescence intensity, DSA IgG3 positivity and C1q binding capacity adequately reclassified patients at lower or higher risk for allograft loss at transplant (category-free net reclassification index, 1.30; 95% CI, 0.94 to 1.67; P<0.001 and 0.93; 95% CI, 0.49 to 1.36; P<0.001, respectively) and post-transplant (category-free net reclassification index, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.62; P<0.001 and 0.95; 95% CI, 0.62 to 1.28; P<0.001, respectively). Thus, pre- and post-transplant DSA monitoring and characterization may improve individual risk stratification for kidney allograft loss.
Keywords: immunology; kidney transplantation; transplant outcomes.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



References
-
- Halloran PF, Schlaut J, Solez K, Srinivasa NS: The significance of the anti-class I response. II. Clinical and pathologic features of renal transplants with anti-class I-like antibody. Transplantation 53: 550–555, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Wiebe C, Gibson IW, Blydt-Hansen TD, Karpinski M, Ho J, Storsley LJ, Goldberg A, Birk PE, Rush DN, Nickerson PW: Evolution and clinical pathologic correlations of de novo donor-specific HLA antibody post kidney transplant. Am J Transplant 12: 1157–1167, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Everly MJ: Update on alloantibodies in solid organ transplantation. Clin Transpl 2014: 125–129, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Reinsmoen NL, Nelson K, Zeevi A: Anti-HLA antibody analysis and crossmatching in heart and lung transplantation. Transpl Immunol 13: 63–71, 2004 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

