Variable Cyst Development in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: The Biologic Context
- PMID: 27493259
- PMCID: PMC5118495
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2016040425
Variable Cyst Development in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: The Biologic Context
Abstract
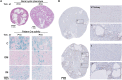
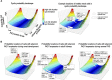
Patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) typically carry a mutation in either the PKD1 or PKD2 gene, which leads to massive cyst formation in both kidneys. However, the large intrafamilial variation in the progression rate of ADPKD suggests involvement of additional factors other than the type of mutation. The identification of these factors will increase our understanding of ADPKD and could ultimately help in the development of a clinically relevant therapy. Our review addresses the mechanisms by which various biologic processes influence cyst formation and cyst growth, thereby explaining an important part of the inter- and intrafamilial variability in ADPKD. Numerous studies from many laboratories provide compelling evidence for the influence on cyst formation by spatiotemporal gene inactivation, the genetic context, the metabolic status, the presence of existing cysts, and whether the kidneys were challenged by renal injury. Collectively, a solid basis is provided for the concept that the probability of cyst formation is determined by functional PKD protein levels and the biologic context. We model these findings in a graphic representation called the cystic probability landscape, providing a robust conceptual understanding of why cells sometimes do or do not form cysts.
Keywords: ADPKD; Biological Context; PKD1; Polycystin; Probability Landscape; polycystic kidney disease.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Peters DJM, Sandkuijl LA: Genetic heterogeneity of polycystic kidney disease in Europe. In: Contributions to Nephrology, Vol. 97: Polycystic Kidney Disease, edited by Breuning MH, Devoto M, Romeo G, Basel, Switzerland, Karger, 1992, pp 128–139 - PubMed
-
- The European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium : The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell 77: 881–894, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Mochizuki T, Wu G, Hayashi T, Xenophontos SL, Veldhuisen B, Saris JJ, Reynolds DM, Cai Y, Gabow PA, Pierides A, Kimberling WJ, Breuning MH, Deltas CC, Peters DJM, Somlo S: PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes an integral membrane protein. Science 272: 1339–1342, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Gabow PA: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease--more than a renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 16: 403–413, 1990 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

