Discriminative Stimulus Effects of Binary Drug Mixtures: Studies with Cocaine, MDPV, and Caffeine
- PMID: 27493274
- PMCID: PMC5034708
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.116.234252
Discriminative Stimulus Effects of Binary Drug Mixtures: Studies with Cocaine, MDPV, and Caffeine
Abstract
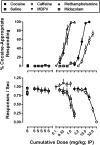
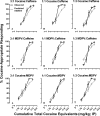
Illicit drug preparations often include more than one pharmacologically active compound. For example, cocaine and synthetic cathinones [e.g., 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV)] are often mixed with caffeine before sale. Caffeine is likely added to these preparations because it is inexpensive and legal; however, caffeine might also mimic or enhance some of the effects of cocaine or MDPV. In these studies, male Sprague-Dawley rats were trained to discriminate 10 mg/kg cocaine from saline, and the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine, caffeine, and MDPV were evaluated alone and as binary mixtures (cocaine and caffeine, MDPV and caffeine, and cocaine and MDPV) at fixed-dose ratios of 3:1, 1:1, and 1:3 relative to the dose of each drug that produced 50% cocaine-appropriate responding. Dose-addition analyses were used to determine the nature of the drug-drug interactions for each mixture (e.g., additive, supra-additive, or subadditive). Although additive interactions were observed for most mixtures, supra-additive interactions were observed at the 50% effect level for the 1:1 mixture of cocaine and caffeine and at the 80% effect level for all three mixtures of cocaine and caffeine, as well as for the 3:1 and 1:3 mixtures of cocaine and MDPV. These results demonstrate that with respect to cocaine-like discriminative stimulus effects, caffeine can function as a substitute in drug preparations containing either cocaine or MDPV, with enhancements of cocaine-like effects possible under certain conditions. Further research is needed to determine whether similar interactions exist for other abuse-related or toxic effects of drug preparations, including cocaine, synthetic cathinones, and caffeine.
U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright.
Figures

References
-
- Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Lehner KR, Thorndike EB, Hoffman AF, Holy M, Rothman RB, Goldberg SR, Lupica CR, Sitte HH, et al. (2013) Powerful cocaine-like actions of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), a principal constituent of psychoactive ‘bath salts’ products. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:552–562. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernardo NP, Siqueira MEPB, DePaiva MJN, Maia PP. (2003) Caffeine and other adulterants in seizures of street cocaine in Brazil. Int J Drug Policy 14:331–334.
-
- Brandt SD, Sumnall HR, Measham F, Cole J. (2010) Analyses of second-generation ‘legal highs’ in the UK: initial findings. Drug Test Anal 2:377–382. - PubMed
-
- Caudevilla-Gálligo F, Ventura M, Indave Ruiz BI, Fornís I, Fornís I. (2013) Presence and composition of cathinone derivatives in drug samples taken from a drug test service in Spain (2010-2012). Hum Psychopharmacol 28:341–344. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

