Microbial rhodopsins: wide distribution, rich diversity and great potential
- PMID: 27493861
- PMCID: PMC4736836
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysico.12.0_121
Microbial rhodopsins: wide distribution, rich diversity and great potential
Abstract
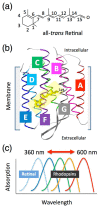
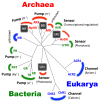
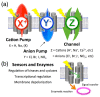
One of the major topics in biophysics and physicobiology is to understand and utilize biological functions using various advanced techniques. Taking advantage of the photoreactivity of the seven-transmembrane rhodopsin protein family has been actively investigated by a variety of methods. Rhodopsins serve as models for membrane-embedded proteins, for photoactive proteins and as a fundamental tool for optogenetics, a new technology to control biological activity with light. In this review, we summarize progress of microbial rhodopsin research from the viewpoint of distribution, diversity and potential.
Keywords: retinal; rhodopsin; visible light; vitamin-A; π-conjugation.
Figures


References
-
- Sudo Y. CRC Handbook of Org Photochem Photobiol. 3rd eds. CRC Press; Boca Raton: 2012. Transport and sensory rhodopsins in microorganisms; pp. 1173–1193.
-
- Spudich JL, Yang CS, Jung KH.&Spudich EN. Retinylidene proteins: structures and functions from archaea to humans. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:365–392. - PubMed
-
- Brown LS. Eubacterial rhodopsins—unique photosensors and diverse ion pumps. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1837:553–561. - PubMed
-
- Brown LS.&Jung KH. Bacteriorhodopsin-like proteins of eubacteria and fungi: the extent of conservation of the haloarchaeal proton-pumping mechanism. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2006;5:538–546. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
