Strain Mediated Adaptation Is Key for Myosin Mechanochemistry: Discovering General Rules for Motor Activity
- PMID: 27494025
- PMCID: PMC4975490
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005035
Strain Mediated Adaptation Is Key for Myosin Mechanochemistry: Discovering General Rules for Motor Activity
Abstract
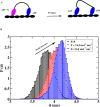
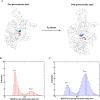
A structure-based model of myosin motor is built in the same spirit of our early work for kinesin-1 and Ncd towards physical understanding of its mechanochemical cycle. We find a structural adaptation of the motor head domain in post-powerstroke state that signals faster ADP release from it compared to the same from the motor head in the pre-powerstroke state. For dimeric myosin, an additional forward strain on the trailing head, originating from the postponed powerstroke state of the leading head in the waiting state of myosin, further increases the rate of ADP release. This coordination between the two heads is the essence of the processivity of the cycle. Our model provides a structural description of the powerstroke step of the cycle as an allosteric transition of the converter domain in response to the Pi release. Additionally, the variation in structural elements peripheral to catalytic motor domain is the deciding factor behind diverse directionalities of myosin motors (myosin V & VI). Finally, we observe that there are general rules for functional molecular motors across the different families. Allosteric structural adaptation of the catalytic motor head in different nucleotide states is crucial for mechanochemistry. Strain-mediated coordination between motor heads is essential for processivity and the variation of peripheral structural elements is essential for their diverse functionalities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Reedy MC. Visualizing myosin’s power stroke in muscle contraction. J Cell Sci. 2000; 113: 3551–3562 - PubMed
-
- Goldman YE. Wag the tail: structural dynamics of actomyosin. Cell.1998; 93: 1–4. - PubMed
-
- De La Cruz EM, Ostap EM. Relating biochemistry and function in the myosin superfamily. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:61–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

