Lin28A activates androgen receptor via regulation of c-myc and promotes malignancy of ER-/Her2+ breast cancer
- PMID: 27494865
- PMCID: PMC5312392
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11004
Lin28A activates androgen receptor via regulation of c-myc and promotes malignancy of ER-/Her2+ breast cancer
Abstract
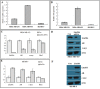
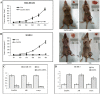
Having previously demonstrated the co-expression status of the Lin28A and androgen receptor (AR) in ER-/Her2+ breast cancer, we tested the hypothesis that Lin28A can activate AR and promotes growth of ER-/Her2+ breast cancer. The expression of Lin28A and AR were examined after Lin28A siRNA and Lin28A plasmid were transfected into ER-/Her2+ breast cancer cells. Chromatin immune-precipitation (ChIP) analysis and Luciferase Assays were used to evaluate the effect of Lin28A and c-myc on AR promoter activity. MTT assays, Boyden chamber invasion assays, colony formation assays and flow cytometry analysis were performed. ER-/Her2+ breast cancer cells which transfected with Lin28A siRNAs and Lin28A plasmid were injected into nude mice, and tumorigenesis was monitored. Our data showed that Lin28A can induced AR expression in ER-/Her2+ breast cancer cells. ChIP analysis showed that Lin28A stimulates the recruitment of c-Myc to the promoter of the AR gene. Lin28A enhanced growth ability, colonies ability, cells proliferation activities, invasive ability and inhibited cells apoptosis of ER-/Her2+ breast cancer cells. Lin28A high expression cells exhibited significantly higher tumorigenic ability in vivo. Our study demonstrates that Lin28A can activates androgen receptor via regulation of c-myc and promotes malignancy of ER-/Her2+ breast cancer. Our findings underline a novel role for Lin28A in breast cancer development and activation of the AR axis.
Keywords: Her2; Lin28A; androgen receptor; breast cancer; c-myc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lin28A and androgen receptor expression in ER-/Her2+ breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Feb;156(1):135-47. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3744-9. Epub 2016 Mar 5. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26944953
-
AR-PDEF pathway promotes tumour proliferation and upregulates MYC-mediated gene transcription by promoting MAD1 degradation in ER-negative breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2018 Sep 14;17(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0883-0. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30217192 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen Receptor Expression and Bicalutamide Antagonize Androgen Receptor Inhibit β-Catenin Transcription Complex in Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(6):2212-2225. doi: 10.1159/000484300. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29069648
-
Androgen receptor signaling pathways as a target for breast cancer treatment.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016 Oct;23(10):R485-98. doi: 10.1530/ERC-16-0190. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27528625 Review.
-
How to target estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer?Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003 Jun;10(2):261-6. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0100261. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12790787 Review.
Cited by
-
MEG3, as a Competing Endogenous RNA, Binds with miR-27a to Promote PHLPP2 Protein Translation and Impairs Bladder Cancer Invasion.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Jun 7;16:51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.01.014. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 30826633 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00355 Promotes the Development and Progression of Colorectal Cancer by Elevating Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor T Expression via RNA Binding Protein lin-28 Homolog A.Front Oncol. 2020 Dec 14;10:582669. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.582669. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33381451 Free PMC article.
-
PP2A as the Main Node of Therapeutic Strategies and Resistance Reversal in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Molecules. 2017 Dec 20;22(12):2277. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122277. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29261144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LIN28A-stabilized FBXL19-AS1 promotes breast cancer migration, invasion and EMT by regulating WDR66.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019 Jun;55(6):426-435. doi: 10.1007/s11626-019-00361-4. Epub 2019 May 28. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019. PMID: 31140103
-
LIN 28B expression is downregulated in mature spermatozoa of oligozoospermic men and associates with genetic variants previously linked to pubertal onset.Endocr Connect. 2025 May 28;14(6):e250044. doi: 10.1530/EC-25-0044. Print 2025 Jun 1. Endocr Connect. 2025. PMID: 40310608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Putti TC, El-Rehim DM, Rakha EA, Paish CE, Lee AH, Pinder SE, Ellis IO. Estrogen receptor–negative breast carcinomas: a review of morphology and immunophenotypical analysis. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:26–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

