Measuring inter-rater reliability for nominal data - which coefficients and confidence intervals are appropriate?
- PMID: 27495131
- PMCID: PMC4974794
- DOI: 10.1186/s12874-016-0200-9
Measuring inter-rater reliability for nominal data - which coefficients and confidence intervals are appropriate?
Abstract
Background: Reliability of measurements is a prerequisite of medical research. For nominal data, Fleiss' kappa (in the following labelled as Fleiss' K) and Krippendorff's alpha provide the highest flexibility of the available reliability measures with respect to number of raters and categories. Our aim was to investigate which measures and which confidence intervals provide the best statistical properties for the assessment of inter-rater reliability in different situations.
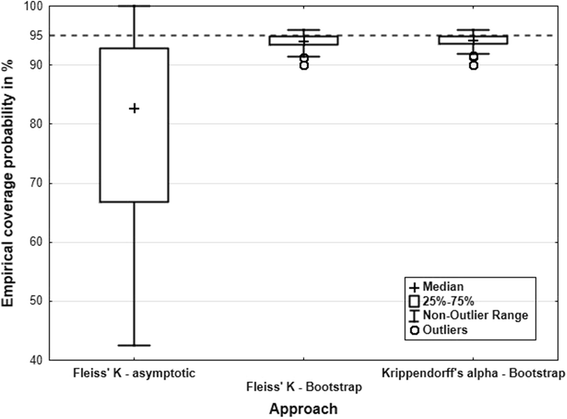
Methods: We performed a large simulation study to investigate the precision of the estimates for Fleiss' K and Krippendorff's alpha and to determine the empirical coverage probability of the corresponding confidence intervals (asymptotic for Fleiss' K and bootstrap for both measures). Furthermore, we compared measures and confidence intervals in a real world case study.
Results: Point estimates of Fleiss' K and Krippendorff's alpha did not differ from each other in all scenarios. In the case of missing data (completely at random), Krippendorff's alpha provided stable estimates, while the complete case analysis approach for Fleiss' K led to biased estimates. For shifted null hypotheses, the coverage probability of the asymptotic confidence interval for Fleiss' K was low, while the bootstrap confidence intervals for both measures provided a coverage probability close to the theoretical one.
Conclusions: Fleiss' K and Krippendorff's alpha with bootstrap confidence intervals are equally suitable for the analysis of reliability of complete nominal data. The asymptotic confidence interval for Fleiss' K should not be used. In the case of missing data or data or higher than nominal order, Krippendorff's alpha is recommended. Together with this article, we provide an R-script for calculating Fleiss' K and Krippendorff's alpha and their corresponding bootstrap confidence intervals.
Keywords: Bootstrap; Confidence interval; Fleiss’ K; Fleiss’ kappa; Inter-rater heterogeneity; Krippendorff’s alpha.
Figures



References
-
- Gwet KL. Handbook of Inter-Rater Reliability. 3. USA: Advanced Analytics, LLC; 2012.
-
- Roger VL, Boerwinkle E, Crapo JD, et al. Strategic transformation of population studies: recommendations of the working group on epidemiology and population sciences from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Advisory Council and Board of External Experts. Am J Epidemiol. 2015;181(6):363–8. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwv011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scott WA. Reliability of content analysis: the case of nominal scale coding. Public Opinion Quarterly. 1955;XIX:321–5. doi: 10.1086/266577. - DOI
-
- Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas. 1960;20:37–46. doi: 10.1177/001316446002000104. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

