Point-of-care C-reactive protein testing to reduce inappropriate use of antibiotics for non-severe acute respiratory infections in Vietnamese primary health care: a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 27495137
- PMCID: PMC4985565
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(16)30142-5
Point-of-care C-reactive protein testing to reduce inappropriate use of antibiotics for non-severe acute respiratory infections in Vietnamese primary health care: a randomised controlled trial
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Glob Health 2016; 4: e633-41.Lancet Glob Health. 2017 Jan;5(1):e39. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(16)30340-0. Lancet Glob Health. 2017. PMID: 27955786 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Inappropriate antibiotic use for acute respiratory tract infections is common in primary health care, but distinguishing serious from self-limiting infections is difficult, particularly in low-resource settings. We assessed whether C-reactive protein point-of-care testing can safely reduce antibiotic use in patients with non-severe acute respiratory tract infections in Vietnam.
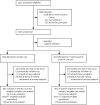
Method: We did a multicentre open-label randomised controlled trial in ten primary health-care centres in northern Vietnam. Patients aged 1-65 years with at least one focal and one systemic symptom of acute respiratory tract infection were assigned 1:1 to receive either C-reactive protein point-of-care testing or routine care, following which antibiotic prescribing decisions were made. Patients with severe acute respiratory tract infection were excluded. Enrolled patients were reassessed on day 3, 4, or 5, and on day 14 a structured telephone interview was done blind to the intervention. Randomised assignments were concealed from prescribers and patients but not masked as the test result was used to assist treatment decisions. The primary outcome was antibiotic use within 14 days of follow-up. All analyses were prespecified in the protocol and the statistical analysis plan. All analyses were done on the intention-to-treat population and the analysis of the primary endpoint was repeated in the per-protocol population. This trial is registered under number NCT01918579.
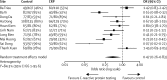
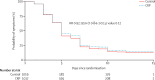
Findings: Between March 17, 2014, and July 3, 2015, 2037 patients (1028 children and 1009 adults) were enrolled and randomised. One adult patient withdrew immediately after randomisation. 1017 patients were assigned to receive C-reactive protein point-of-care testing, and 1019 patients were assigned to receive routine care. 115 patients in the C-reactive protein point-of-care group and 72 patients in the routine care group were excluded in the intention-to-treat analysis due to missing primary endpoint. The number of patients who used antibiotics within 14 days was 581 (64%) of 902 patients in the C-reactive protein group versus 738 (78%) of 947 patients in the control group (odds ratio [OR] 0·49, 95% CI 0·40-0·61; p<0·0001). Highly significant differences were seen in both children and adults, with substantial heterogeneity of the intervention effect across the 10 sites (I(2)=84%, 95% CI 66-96). 140 patients in the C-reactive protein group and 137 patients in the routine care group missed the urine test on day 3, 4, or 5. Antibiotic activity in urine on day 3, 4, or 5 was found in 267 (30%) of 877 patients in the C-reactive protein group versus 314 (36%) of 882 patients in the routine treatment group (OR 0·78, 95% CI 0·63-0·95; p=0·015). Time to resolution of symptoms was similar in both groups. Adverse events were rare, with no deaths and a total of 14 hospital admissions (six in the C-reactive protein group and eight in the control group).
Interpretation: C-reactive protein point-of-care testing reduced antibiotic use for non-severe acute respiratory tract infection without compromising patients' recovery in primary health care in Vietnam. Health-care providers might have become familiar with the clinical picture of low C-reactive protein, leading to reduction in antibiotic prescribing in both groups, but this would have led to a reduction in observed effect, rather than overestimation. Qualitative analysis is needed to address differences in context in order to implement this strategy to improve rational antibiotic use for patients with acute respiratory infection in low-income and middle-income countries.
Funding: Wellcome Trust, UK, and Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership, USA.
Copyright © 2016 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Biomarker-guided antibiotic use in primary care in resource-constrained environments.Lancet Glob Health. 2016 Sep;4(9):e586-7. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(16)30170-X. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Lancet Glob Health. 2016. PMID: 27495136 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization's strategy to contain resistance to antimicrobial drugs. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2001;10:284–294. (in Spanish). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

