Treadmill exercise within lower body negative pressure protects leg lean tissue mass and extensor strength and endurance during bed rest
- PMID: 27495299
- PMCID: PMC4985554
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12892
Treadmill exercise within lower body negative pressure protects leg lean tissue mass and extensor strength and endurance during bed rest
Abstract
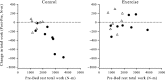
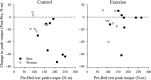
Leg muscle mass and strength are decreased during reduced activity and non-weight-bearing conditions such as bed rest (BR) and spaceflight. Supine treadmill exercise within lower body negative pressure (LBNPEX) provides full-body weight loading during BR and may prevent muscle deconditioning. We hypothesized that a 40-min interval exercise protocol performed against LBNPEX 6 days week(-1) would attenuate losses in leg lean mass (LLM), strength, and endurance during 6° head-down tilt BR, with similar benefits for men and women. Fifteen pairs of healthy monozygous twins (8 male and 7 female pairs) completed 30 days of BR with one sibling of each twin pair assigned randomly as the non-exercise control (CON) and the other twin as the exercise subject (EX). Before and after BR, LLM and isokinetic leg strength and endurance were measured. Mean knee and ankle extensor and flexor strength and endurance and LLM decreased from pre- to post-BR in the male CON subjects (P < 0.01), but knee extensor strength and endurance, ankle extensor strength, and LLM were maintained in the male EX subjects. In contrast, no pre- to post-BR changes were significant in the female subjects, either CON or EX, likely due to their lower pre-BR values. Importantly, the LBNPEX countermeasure prevents or attenuates declines in LLM as well as extensor leg strength and endurance. Individuals who are stronger, have higher levels of muscular endurance, and/or have greater LLM are likely to experience greater losses during BR than those who are less fit.
Keywords: Body composition; head down tilt; isokinetic; microgravity; muscle atrophy; spaceflight.
© 2016 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
WISE-2005: Countermeasures to prevent muscle deconditioning during bed rest in women.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014 Mar 15;116(6):654-67. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00590.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014. PMID: 24458754 Clinical Trial.
-
Musculoskeletal effects of 5 days of bed rest with and without locomotion replacement training.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015 Apr;115(4):727-38. doi: 10.1007/s00421-014-3045-0. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25425257 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
LBNP treadmill exercise maintains spine function and muscle strength in identical twins during 28-day simulated microgravity.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007 Jun;102(6):2274-8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00541.2006. Epub 2007 Mar 29. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007. PMID: 17395762
-
Nutritional interventions during bed rest and spaceflight: prevention of muscle mass and strength loss, bone resorption, glucose intolerance, and cardiovascular problems.Nutr Res. 2020 Oct;82:11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Nutr Res. 2020. PMID: 32890860 Review.
-
Implementation of exercise countermeasures during spaceflight and microgravity analogue studies: Developing countermeasure protocols for bedrest in older adults (BROA).Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 9;13:928313. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.928313. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36017336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Towards human exploration of space: the THESEUS review series on muscle and bone research priorities.NPJ Microgravity. 2017 Feb 14;3:8. doi: 10.1038/s41526-017-0013-0. eCollection 2017. NPJ Microgravity. 2017. PMID: 28649630 Free PMC article.
-
Nonuniform loss of muscle strength and atrophy during bed rest: a systematic review.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021 Jul 1;131(1):194-206. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00363.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021. PMID: 33703945 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Constraint Loading on the Lower Limb Muscle Forces in Weightless Treadmill Exercise.J Healthc Eng. 2018 Apr 3;2018:8487308. doi: 10.1155/2018/8487308. eCollection 2018. J Healthc Eng. 2018. PMID: 29850002 Free PMC article.
-
Cardio-postural interactions and muscle-pump baroreflex are severely impacted by 60-day bedrest immobilization.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 21;10(1):12042. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68962-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32694819 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation to microgravity, deconditioning, and countermeasures.J Physiol Sci. 2017 Mar;67(2):271-281. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0514-8. Epub 2016 Dec 20. J Physiol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28000175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams, G. R. , Caiozzo V. J., and Baldwin K. M.. 2003. Skeletal muscle unweighting: spaceflight and ground‐based models. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 95:2185–2201. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, K. M. , White T. P., Arnaud S. B., Edgerton V. R., Kraemer W. J., Kram R., et al. 1996. Musculoskeletal adaptations to weightlessness and development of effective countermeasures. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 28:1247–1253. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini, Y. , Krieger A. M., and Yekutieli D.. 2006. Adaptive linear step‐up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika 93:491–507.
-
- Blanc, S. , Normand S., Pachiaudi C., Fortrat J. O., Laville M., and Gharib C.. 2000. Fuel homeostasis during physical inactivity induced by bed rest. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85:2223–2233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

