SMARCE1 regulates metastatic potential of breast cancer cells through the HIF1A/PTK2 pathway
- PMID: 27495308
- PMCID: PMC4974701
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-016-0738-9
SMARCE1 regulates metastatic potential of breast cancer cells through the HIF1A/PTK2 pathway
Abstract
Background: While aberrant activation of the chromatin-remodeling SWI/SNF complexes has been associated with cancer development and progression, the role of each subunit in tumor cells is poorly defined. This study is aimed to characterize the role of SMARCE1/BAF57 in regulating metastasis of breast cancer cells.
Methods: Genetic approaches and chemical inhibitors were used to manipulate the activities of SMARCE1 and its downstream targets in multiple breast cancer cell lines. Xenograft mouse models were used to analyze the role of SMARCE1 in lung metastasis in vivo. Nonadherent culture conditions were used to elucidate the role of SMARCE1 in regulating anoikis. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), immunoprecipitation, and immunoblotting assays were designed to dissect the mechanism of action of SMARCE1. Public databases were used to investigate the relationship between SMARCE1 deregulation and breast cancer prognosis.
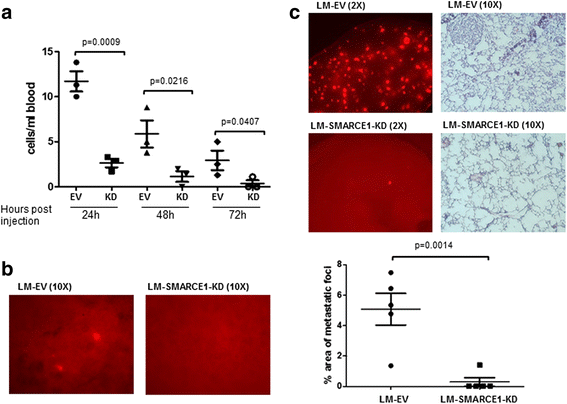
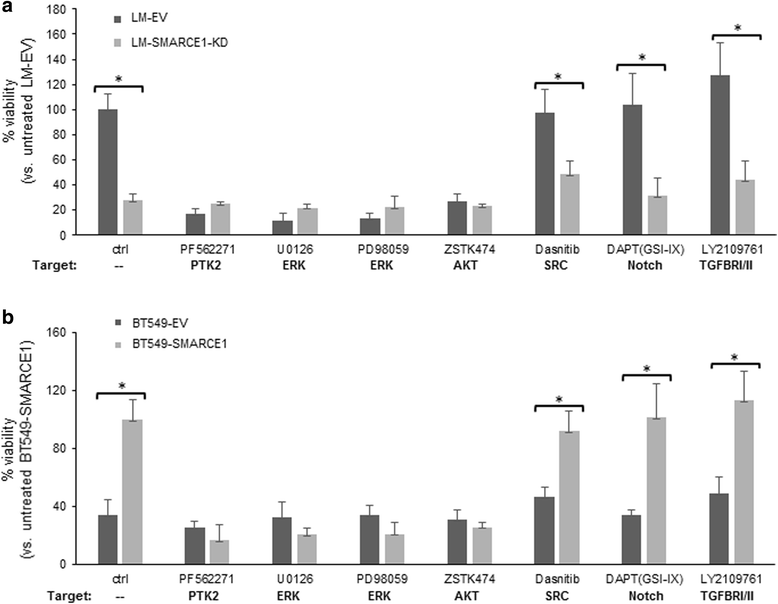
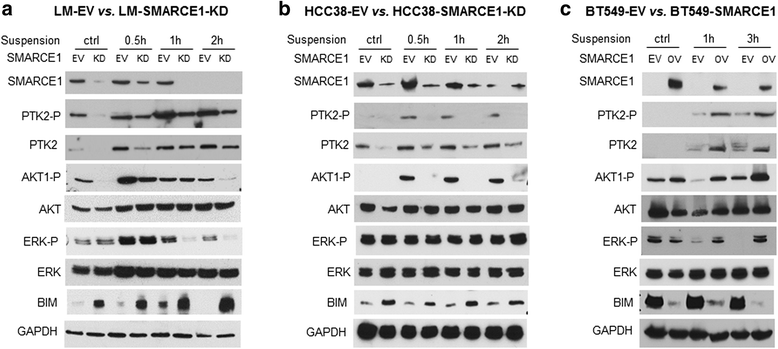
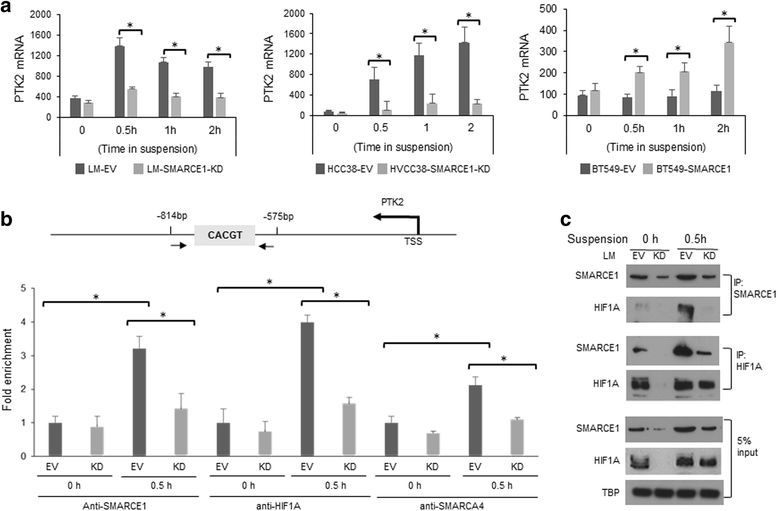
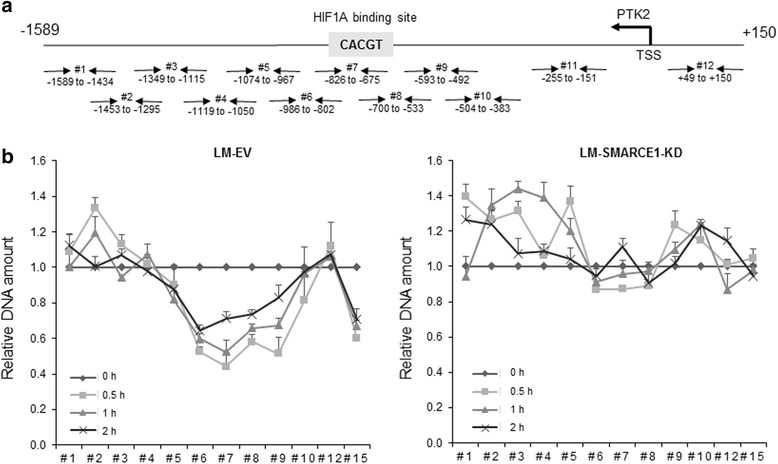
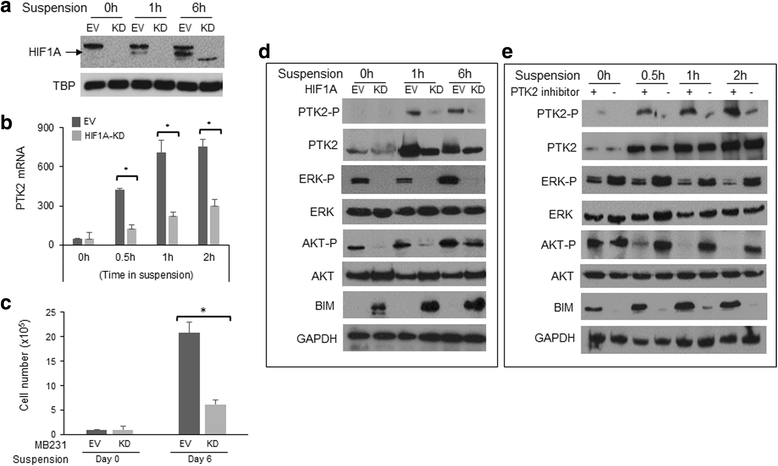
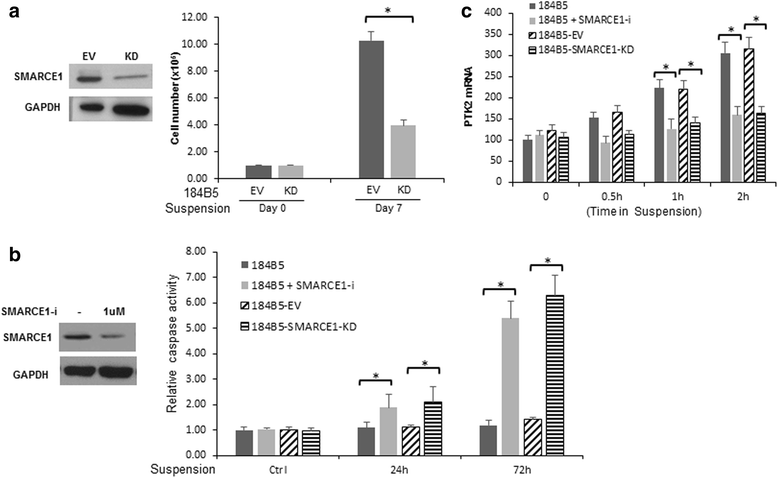
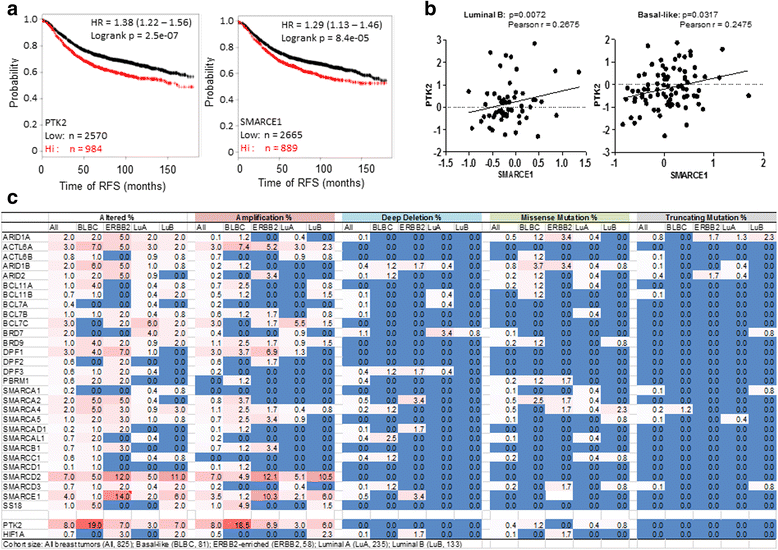
Results: SMARCE1 knockdown reduced lung metastasis of breast cancer cells and sensitized tumor cells to anoikis. In response to loss of attachment, SMARCE1 interacted with and potentiated transcriptional activity of HIF1A, resulting in rapid PTK2 activation. Both HIF1A and PTK2 were indispensable for SMARCE1-mediated protection against anoikis by promoting activation of ERK and AKT pathways while suppressing the expression of pro-apoptotic BIM protein. Expression data analysis of a large cohort of human breast tumors revealed that high expression of SMARCE1 or PTK2 is associated with poor prognosis and tumor relapse, and PTK2 expression is positively correlated with SMARCE1 expression in basal-like and luminal B subtypes of breast tumors.
Conclusions: SMARCE1 plays an essential role in breast cancer metastasis by protecting cells against anoikis through the HIF1A/PTK2 pathway. SMARCE1-mediated PTK2 activation likely plays a key role in promoting metastasis of basal-like and luminal B subtype of breast tumors.
Keywords: Anoikis; Breast cancer; HIF1A; PTK2/FAK; SMARCE1/BAF57.
Figures



References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2016. 2016. http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstati.
-
- Labelle M, Hynes RO. The initial hours of metastasis: the importance of cooperative host-tumor cell interactions during hematogenous dissemination. Cancer Discov. 2012;2(12):1091–1099. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0329. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

