The AIM2-like Receptors Are Dispensable for the Interferon Response to Intracellular DNA
- PMID: 27496731
- PMCID: PMC4988931
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.06.015
The AIM2-like Receptors Are Dispensable for the Interferon Response to Intracellular DNA
Abstract
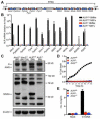
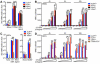
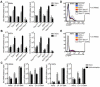
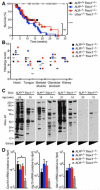
Detection of intracellular DNA triggers activation of the STING-dependent interferon-stimulatory DNA (ISD) pathway, which is essential for antiviral responses. Multiple DNA sensors have been proposed to activate this pathway, including AIM2-like receptors (ALRs). Whether the ALRs are essential for activation of this pathway remains unknown. To rigorously explore the function of ALRs, we generated mice lacking all 13 ALR genes. We found that ALRs are dispensable for the type I interferon (IFN) response to transfected DNA ligands, DNA virus infection, and lentivirus infection. We also found that ALRs do not contribute to autoimmune disease in the Trex1(-/-) mouse model of Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome. Finally, CRISPR-mediated disruption of the human AIM2-like receptor IFI16 in primary fibroblasts revealed that IFI16 is not essential for the IFN response to human cytomegalovirus infection. Our findings indicate that ALRs are dispensable for the ISD response and suggest that alternative functions for these receptors should be explored.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
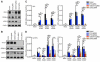

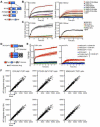
Comment in
-
Cytosolic DNA Sensing: The Field Narrows.Immunity. 2016 Aug 16;45(2):227-8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.08.006. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 27533006
Similar articles
-
Cutting Edge: cGAS Is Required for Lethal Autoimmune Disease in the Trex1-Deficient Mouse Model of Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):1939-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500969. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26223655 Free PMC article.
-
AIM2-Like Receptors Positively and Negatively Regulate the Interferon Response Induced by Cytosolic DNA.mBio. 2017 Jul 5;8(4):e00944-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00944-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28679751 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA sensors AIM2 and IFI16 are SLE autoantigens that bind neutrophil extracellular traps.Elife. 2022 May 24;11:e72103. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72103. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35608258 Free PMC article.
-
The Absent in Melanoma 2-Like Receptor IFN-Inducible Protein 16 as an Inflammasome Regulator in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Dark Side of Sensing Microbes.Front Immunol. 2018 May 28;9:1180. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01180. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29892303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular Nucleic Acid Detection in Autoimmunity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2017 Apr 26;35:313-336. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052331. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28142323 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleic Acid Immunity in the Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 16;10:1636. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01636. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31379837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Protein UL94 Targets MITA to Evade the Antiviral Immune Response.J Virol. 2020 Jun 1;94(12):e00022-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00022-20. Print 2020 Jun 1. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32238587 Free PMC article.
-
A Variety of Mouse PYHIN Proteins Restrict Murine and Human Retroviruses.Viruses. 2024 Mar 23;16(4):493. doi: 10.3390/v16040493. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675836 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV strategies for host dsDNA sensing machinery.Virol Sin. 2016 Dec;31(6):466-471. doi: 10.1007/s12250-016-3877-3. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Virol Sin. 2016. PMID: 27933565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Central Role of IFI204 in IFN-β Release and Autophagy Activation during Mycobacterium bovis Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 5;7:169. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00169. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28529930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burckstummer T, Baumann C, Bluml S, Dixit E, Durnberger G, Jahn H, Planyavsky M, Bilban M, Colinge J, Bennett KL, Superti-Furga G. An orthogonal proteomic-genomic screen identifies AIM2 as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor for the inflammasome. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:266–272. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

