Protein Kinase A Subunit Balance Regulates Lipid Metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans and Mammalian Adipocytes
- PMID: 27496951
- PMCID: PMC5034032
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.740464
Protein Kinase A Subunit Balance Regulates Lipid Metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans and Mammalian Adipocytes
Abstract
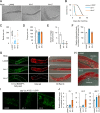
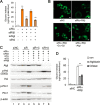
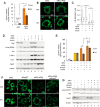
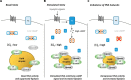
Protein kinase A (PKA) is a cyclic AMP (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase composed of catalytic and regulatory subunits and involved in various physiological phenomena, including lipid metabolism. Here we demonstrated that the stoichiometric balance between catalytic and regulatory subunits is crucial for maintaining basal PKA activity and lipid homeostasis. To uncover the potential roles of each PKA subunit, Caenorhabditis elegans was used to investigate the effects of PKA subunit deficiency. In worms, suppression of PKA via RNAi resulted in severe phenotypes, including shortened life span, decreased egg laying, reduced locomotion, and altered lipid distribution. Similarly, in mammalian adipocytes, suppression of PKA regulatory subunits RIα and RIIβ via siRNAs potently stimulated PKA activity, leading to potentiated lipolysis without increasing cAMP levels. Nevertheless, insulin exerted anti-lipolytic effects and restored lipid droplet integrity by antagonizing PKA action. Together, these data implicate the importance of subunit stoichiometry as another regulatory mechanism of PKA activity and lipid metabolism.
Keywords: adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL); lipid droplet; lipolysis; protein kinase A (PKA); stoichiometry.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Berthet J., Sutherland E. W., and Rall T. W. (1957) The assay of glucagon and epinephrine with use of liver homogenates. J. Biol. Chem. 229, 351–361 - PubMed
-
- Rall T. W., and Sutherland E. W. (1958) Formation of a cyclic adenine ribonucleotide by tissue particles. J. Biol. Chem. 232, 1065–1076 - PubMed
-
- Sutherland E. W., and Rall T. W. (1958) Fractionation and characterization of a cyclic adenine ribonucleotide formed by tissue particles. J. Biol. Chem. 232, 1077–1091 - PubMed
-
- Krebs E. G., Graves D. J., and Fischer E. H. (1959) Factors affecting the activity of muscle phosphorylase B kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 234, 2867–2873 - PubMed
-
- Reimann E. M., Brostrom C. O., Corbin J. D., King C. A., and Krebs E. G. (1971) Separation of regulatory and catalytic subunits of the cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase(s) of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 42, 187–194 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

