N-Terminal Peptide Detection with Optimized Peptide-Spectrum Matching and Streamlined Sequence Libraries
- PMID: 27498768
- PMCID: PMC7379158
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00996
N-Terminal Peptide Detection with Optimized Peptide-Spectrum Matching and Streamlined Sequence Libraries
Abstract
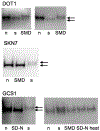
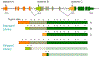
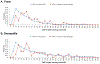
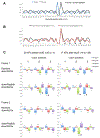
We identified tryptic peptides in yeast cell lysates that map to translation initiation sites downstream of the annotated start sites using the peptide-spectrum matching algorithms OMSSA and Mascot. To increase the accuracy of peptide-spectrum matching, both algorithms were run using several standardized parameter sets, and Mascot was run utilizing a, b, and y ions from collision-induced dissociation. A large fraction (22%) of the detected N-terminal peptides mapped to translation initiation downstream of the annotated initiation sites. Expression of several truncated proteins from downstream initiation in the same reading frame as the full-length protein (frame 1) was verified by western analysis. To facilitate analysis of the larger proteome of Drosophila, we created a streamlined sequence library from which all duplicated trypsin fragments had been removed. OMSSA assessment using this "stripped" library revealed 171 peptides that map to downstream translation initiation sites, 76% of which are in the same reading frame as the full-length annotated proteins, although some are in different reading frames creating new protein sequences not in the annotated proteome. Sequences surrounding implicated downstream AUG start codons are associated with nucleotide preferences with a pronounced three-base periodicity N1^G2^A3.
Keywords: Mascot; OMSSA; peptide mass spectrometry; streamlined sequence libraries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amino termini of many yeast proteins map to downstream start codons.J Proteome Res. 2012 Dec 7;11(12):5712-9. doi: 10.1021/pr300538f. Epub 2012 Nov 21. J Proteome Res. 2012. PMID: 23140384 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced peptide identification by electron transfer dissociation using an improved Mascot Percolator.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Aug;11(8):478-91. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O111.014522. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22493177 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae N-terminal proteome provides evidence of alternative translation initiation and post-translational N-terminal acetylation.J Proteome Res. 2011 Aug 5;10(8):3578-89. doi: 10.1021/pr2002325. Epub 2011 Jun 20. J Proteome Res. 2011. PMID: 21619078
-
Tandem mass spectral libraries of peptides and their roles in proteomics research.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2017 Sep;36(5):634-648. doi: 10.1002/mas.21512. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2017. PMID: 27403644 Review.
-
Spectral library searching in proteomics.Proteomics. 2016 Mar;16(5):729-40. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201500296. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26616598 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin-sensitive cryptic promoters putatively drive expression of alternative protein isoforms in yeast.Genome Res. 2019 Dec;29(12):1974-1984. doi: 10.1101/gr.243378.118. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 31740578 Free PMC article.
-
A Ribosome Interaction Surface Sensitive to mRNA GCN Periodicity.Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 3;10(6):849. doi: 10.3390/biom10060849. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32503152 Free PMC article.
-
GCN sensitive protein translation in yeast.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 18;15(9):e0233197. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233197. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32946445 Free PMC article.
-
N-terminal Proteomics Assisted Profiling of the Unexplored Translation Initiation Landscape in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Jun;16(6):1064-1080. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.066662. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28432195 Free PMC article.
-
An Internal Promoter Drives the Expression of a Truncated Form of CCC1 Capable of Protecting Yeast from Iron Toxicity.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 20;9(6):1337. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061337. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34203091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eckhard U; Marino G; Abbey SR; Tharmarajah G; Matthew I; Overall CM The Human Dental Pulp Proteome and N-Terminome: Levering the Unexplored Potential ofSemitryptic Peptides Enriched by TAILS to Identify Missing Proteins in the Human Proteome Project in Underexplored Tissues. J. Proteome Res 2015, 14 (9), 3568–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

