Phosphoproteome Integration Reveals Patient-Specific Networks in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 27499020
- PMCID: PMC4985183
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.007
Phosphoproteome Integration Reveals Patient-Specific Networks in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
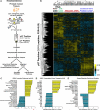
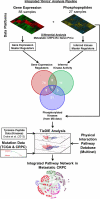
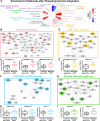
We used clinical tissue from lethal metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) patients obtained at rapid autopsy to evaluate diverse genomic, transcriptomic, and phosphoproteomic datasets for pathway analysis. Using Tied Diffusion through Interacting Events (TieDIE), we integrated differentially expressed master transcriptional regulators, functionally mutated genes, and differentially activated kinases in CRPC tissues to synthesize a robust signaling network consisting of druggable kinase pathways. Using MSigDB hallmark gene sets, six major signaling pathways with phosphorylation of several key residues were significantly enriched in CRPC tumors after incorporation of phosphoproteomic data. Individual autopsy profiles developed using these hallmarks revealed clinically relevant pathway information potentially suitable for patient stratification and targeted therapies in late stage prostate cancer. Here, we describe phosphorylation-based cancer hallmarks using integrated personalized signatures (pCHIPS) that shed light on the diversity of activated signaling pathways in metastatic CRPC while providing an integrative, pathway-based reference for drug prioritization in individual patients.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Alvarez MJ, Giorgi F, Califano A. Using viper, a package for Virtual Inference of Protein-activity by Enriched Regulon analysis. 2015.
-
- Aytes A, Alvaro A, Antonina M, Celine L, Alvarez MJ, Mireia C-M, Tian Z, Eastham JA, Anuradha G, Pienta KJ, et al. Cross-Species Regulatory Network Analysis Identifies a Synergistic Interaction between FOXM1 and CENPF that Drives Prostate Cancer Malignancy. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:638–651. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA195505/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA098010/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA181242/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006097/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM109031/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA092131/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016042/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009120/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA184397/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA180778/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA168585/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA172603/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/HHMI/United States
- R01 GM089778/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA230819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

