Single mode waveguide platform for spontaneous and surface-enhanced on-chip Raman spectroscopy
- PMID: 27499842
- PMCID: PMC4918833
- DOI: 10.1098/rsfs.2016.0015
Single mode waveguide platform for spontaneous and surface-enhanced on-chip Raman spectroscopy
Abstract
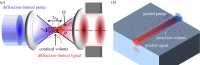
We review an on-chip approach for spontaneous Raman spectroscopy and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy based on evanescent excitation of the analyte as well as evanescent collection of the Raman signal using complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS)-compatible single mode waveguides. The signal is either directly collected from the analyte molecules or via plasmonic nanoantennas integrated on top of the waveguides. Flexibility in the design of the geometry of the waveguide, and/or the geometry of the antennas, enables optimization of the collection efficiency. Furthermore, the sensor can be integrated with additional functionality (sources, detectors, spectrometers) on the same chip. In this paper, the basic theoretical concepts are introduced to identify the key design parameters, and some proof-of-concept experimental results are reviewed.
Keywords: Raman spectroscopy; laboratory on a chip; silicon photonics; surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy; waveguides.
Figures







References
-
- Long DA. 2002. The Raman effect: a unified treatment of the theory of Raman scattering by molecules. West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
-
- Ferraro JR. 2003. Introductory Raman spectroscopy. New York, NY: Academic Press.
-
- Laserna JJ. 1996. Modern techniques in Raman spectroscopy. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
-
- Cialla D, Deckert-Gaudig T, Budich C, Laue M, Möller R, Naumann D, Deckert V, Popp J. 2009. Raman to the limit: tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopic investigations of a single tobacco mosaic virus. J. Raman Spectrosc. 40, 240–243. (10.1002/jrs.2123) - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

