Robotic-assisted thoracoscopic sleeve lobectomy for locally advanced lung cancer
- PMID: 27499965
- PMCID: PMC4958819
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2016.06.14
Robotic-assisted thoracoscopic sleeve lobectomy for locally advanced lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The Da Vinci robotic system has been used to enhance the surgeon's visualization and agility in lung cancer surgery, and thus facilitate refined dissection, knot tying and suturing. However, only a few case reports exist on performing a sleeve lobectomy with a robotic-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS) technique. Here we describe our early experience performing RATS sleeve lobectomies. To our knowledge, this is the first study reporting a series of RATS sleeve lobectomies.
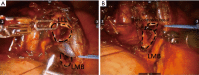
Methods: The six consecutive NSCLC patients who underwent a RATS sleeve lobectomy between November 2013 and July 2015 at the National Taiwan University Hospital were enrolled in this study. The lobectomies were all performed by the same surgeon using a three-arm robotic system with an additional utility incision made for assistance and specimen retrieval.
Results: Five patients were diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, while the sixth was diagnosed with a carcinoid tumor. The mean operation time was 436.7 [255-745] minutes. The mean postoperative intensive care unit (ICU) stay and hospital stay were 3.7 [1-11] and 11.3 [3-26] days, respectively. Two (33.3%; 2/6) morbidities were noted, including one pneumonia and one anastomosis stricture. There were no cases of mortality or of conversion to thoracotomy.
Conclusions: Our experience performing a RATS sleeve lobectomy in the six patients demonstrated the feasibility of RATS in complex lung cancer surgeries. The three-dimensional vision and articulated joint instruments made robotic-assisted bronchial anastomosis easier under the endoscopic setting. Our experience suggests that RATS offers specific advantages with regard to accuracy and safety when performing sleeve lobectomies.
Keywords: Robotic sugery; lung cancer surgery; sleeve lobectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Louie BE, Farivar AS, Aye RW, et al. Early experience with robotic lung resection results in similar operative outcomes and morbidity when compared with matched video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery cases. Ann Thorac Surg 2012;93:1598-604; discussion 1604-5. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.01.067 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
