Comparison of corneal flaps created by Wavelight FS200 and Intralase FS60 femtosecond lasers
- PMID: 27500109
- PMCID: PMC4951655
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2016.07.12
Comparison of corneal flaps created by Wavelight FS200 and Intralase FS60 femtosecond lasers
Abstract
Aim: To assess and compare the morphology of corneal flaps created by the Wavelight FS200 and Intralase FS60 femtosecond lasers in laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK).
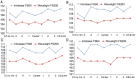
Methods: Four hundred eyes of 200 patients were enrolled in this study and divided into Wavelight FS200 groups (200 eyes) and Intralase FS60 groups (200 eyes). Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography (RTVue OCT) was used to measure the corneal flap thickness of 36 specified measurements on each flap one week after surgery. Results were used to analyze the regularity, uniformity and accuracy of the two types of LASIK flaps.
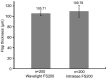
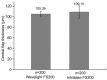
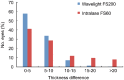
Results: The mean thickness of corneal flap and central flap was 105.71±4.72 µm and 105.39±4.50 µm in Wavelight FS200 group and 109.78±11.42 µm and 109.15 ±11.59 µm in Intralase FS60 group, respectively. The flaps made with the Wavelight FS200 femtosecond laser were thinner than those created by the Intralase FS60 femtosecond laser (P=0.000). Corneal flaps in the 2 groups were uniform and regular, showing an almost planar configuration. But the Wavelight FS200 group has more predictability and uniformity of flap creation. The mean deviation between achieved and attempted flap thickness was smaller in the Wavelight FS200 group than that in the Intralase FS60 group, which were 5.18±3.71 µm and 8.68±7.42 µm respectively. The deviation of more than 20 µm was 0.2% measurements in Wavelight FS200 group and 8.29% measurements in Intralase FS60 group.
Conclusion: The morphologies of flaps created by Wavelight FS200 are more uniform and thinner than those created by Intralase FS60.
Keywords: Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography; Intralase FS60; Wavelight FS200; femtosecond laser; flap; laser in situ keratomileusis.
Figures


References
-
- Sandoval HP, de Castro LE, Vroman DT, Solomon KD. Refractive surgery survey 2004. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31(1):221–233. - PubMed
-
- Sugar A, Rapuano CJ, Culbertson WW, Huang D, Varley GA, Agapitos PJ, de Luise VP, Koch DD. Laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia and astigmatism: safety and efficacy: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2002;109(1):175–187. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Tian L, Wang N, Dougherty PJ. Anterior segment optical coherence tomography measurement of LASIK Flaps: femtosecond laser vs microkeratome. J Refract Surg. 2011;27(6):408–416. - PubMed
-
- Reggiani-Mello G, Krueger RR. Comparison of commercially avail-able femtosecond lasers in refractive surgery. Expert Rev Opthalmol. 2011;6(1):55–65.
-
- Binder PS, Trattler WB. Evaluation of a risk factor scoring system for corneal ectasia after LASIK in eyes with normal topography. J Refract Surg. 2010;26(4):241–250. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
