Genome Sequence of the Edible Cultivated Mushroom Lentinula edodes (Shiitake) Reveals Insights into Lignocellulose Degradation
- PMID: 27500531
- PMCID: PMC4976891
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160336
Genome Sequence of the Edible Cultivated Mushroom Lentinula edodes (Shiitake) Reveals Insights into Lignocellulose Degradation
Abstract
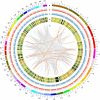
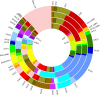
Lentinula edodes, one of the most popular, edible mushroom species with a high content of proteins and polysaccharides as well as unique aroma, is widely cultivated in many Asian countries, especially in China, Japan and Korea. As a white rot fungus with lignocellulose degradation ability, L. edodes has the potential for application in the utilization of agriculture straw resources. Here, we report its 41.8-Mb genome, encoding 14,889 predicted genes. Through a phylogenetic analysis with model species of fungi, the evolutionary divergence time of L. edodes and Gymnopus luxurians was estimated to be 39 MYA. The carbohydrate-active enzyme genes in L. edodes were compared with those of the other 25 fungal species, and 101 lignocellulolytic enzymes were identified in L. edodes, similar to other white rot fungi. Transcriptome analysis showed that the expression of genes encoding two cellulases and 16 transcription factor was up-regulated when mycelia were cultivated for 120 minutes in cellulose medium versus glucose medium. Our results will foster a better understanding of the molecular mechanism of lignocellulose degradation and provide the basis for partial replacement of wood sawdust with agricultural wastes in L. edodes cultivation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Whole genome de novo sequencing and genome annotation of the world popular cultivated edible mushroom, Lentinula edodes.J Biotechnol. 2016 Apr 10;223:24-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.02.032. Epub 2016 Feb 26. J Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26924240
-
Lentinula edodes Genome Survey and Postharvest Transcriptome Analysis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 May 1;83(10):e02990-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02990-16. Print 2017 May 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28314725 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative secretomic analysis of lignocellulose degradation by Lentinula edodes grown on microcrystalline cellulose, lignosulfonate and glucose.J Proteomics. 2017 Jun 23;163:92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.04.023. Epub 2017 May 5. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28483534
-
Cultivation methods and biology of Lentinula edodes.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 11;109(1):63. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13387-w. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40067479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive small secondary metabolites from the mushrooms Lentinula edodes and Flammulina velutipes.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2020 Oct;73(10):687-696. doi: 10.1038/s41429-020-0354-x. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2020. PMID: 32733077 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Antrodia cinnamomea Mycelia from Different Wood Substrates.Mycobiology. 2023 Feb 15;51(1):49-59. doi: 10.1080/12298093.2023.2175434. eCollection 2023. Mycobiology. 2023. PMID: 36846623 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Comparison of Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes (CAZymes) Repertoire of Flammulina ononidis.Mycobiology. 2018 Nov 16;46(4):349-360. doi: 10.1080/12298093.2018.1537585. eCollection 2018. Mycobiology. 2018. PMID: 30637143 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic structure and evolutionary diversity of mating-type (MAT) loci in Hypsizygus marmoreus.IMA Fungus. 2021 Dec 20;12(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s43008-021-00086-8. IMA Fungus. 2021. PMID: 34930496 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous Delta-12 Fatty Acid Desaturase (FAD2) Genes Affect Gene Expression and Linoleic Acid Levels in Lentinula edodes under Heat Stress.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;10(7):496. doi: 10.3390/jof10070496. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39057381 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Sequencing of Lentinula edodes Revealed a Genomic Variant Block Associated with a Thermo-Tolerant Trait in Fruit Body Formation.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Sep 2;10(9):628. doi: 10.3390/jof10090628. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang S-T (1999) World production of cultivated edible and medicinal mushrooms in 1997 with emphasis on Lentinus edodes (Berk.) Sing, in China. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms 1.
-
- Chang S, Miles P (1987) Historical record of the early cultivation of Lentinus in China. Mushroom Journal of the Tropics 7: 31–37.
-
- Sakamoto Y, Minato K-i, Nagai M, Mizuno M, Sato T (2005) Characterization of the Lentinula edodes exg2 gene encoding a lentinan-degrading exo-β-1, 3-glucanase. Current genetics 48: 195–203. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

