Deployment-Associated Exposure Surveillance With High-Resolution Metabolomics
- PMID: 27501099
- PMCID: PMC4978191
- DOI: 10.1097/JOM.0000000000000768
Deployment-Associated Exposure Surveillance With High-Resolution Metabolomics
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the suitability of high-resolution metabolomics (HRM) for measure of internal exposure and effect biomarkers from deployment-related environmental hazards.
Methods: HRM provides extensive coverage of metabolism and data relevant to a broad spectrum of environmental exposures. This review briefly describes the analytic platform, workflow, and recent applications of HRM as a prototype environmental exposure surveillance system.
Results: Building upon techniques available for contemporary occupational medicine and exposure sciences, HRM methods are able to integrate external exposures, internal body burden of environmental agents, and relevant biological responses with health outcomes.
Conclusions: Systematic analysis of existing Department of Defense Serum Repository samples will provide a high-quality, cross-sectional reference dataset for deployment-associated exposures while at the same time establishing a foundation for precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


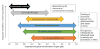
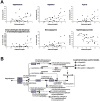
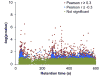

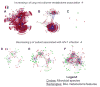
References
-
- Lindler LE. Enhancing the Department of Defense’s Capability to Identify Environmental Exposures Into the 21st Century. Mil Med. 2015;180(10 Suppl):5–9. - PubMed
-
- Tollerud D, et al. Long-Term Health Consequences of Exposure to Burn Pits in Iraq and Afghanistan. Washington DC: 2011. - PubMed
-
- Baird CP. Review of the Institute of Medicine report: long-term health consequences of exposure to burn pits in Iraq and Afghanistan. US Army Med Dep J. 2012:43–7. - PubMed
-
- Perdue CL, Eick-Cost AA, Rubertone MV. A Brief Description of the Operation of the DoD Serum Repository. Mil Med. 2015;180(10 Suppl):10–2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

