High-Resolution Metabolomics Assessment of Military Personnel: Evaluating Analytical Strategies for Chemical Detection
- PMID: 27501105
- PMCID: PMC4978147
- DOI: 10.1097/JOM.0000000000000773
High-Resolution Metabolomics Assessment of Military Personnel: Evaluating Analytical Strategies for Chemical Detection
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to maximize detection of serum metabolites with high-resolution metabolomics (HRM).
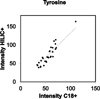
Methods: Department of Defense Serum Repository (DoDSR) samples were analyzed using ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry with three complementary chromatographic phases and four ionization modes. Chemical coverage was evaluated by number of ions detected and accurate mass matches to a human metabolomics database.
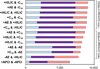
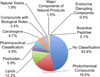
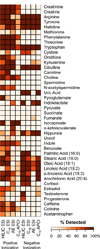
Results: Individual HRM platforms provided accurate mass matches for up to 58% of the KEGG metabolite database. Combining two analytical methods increased matches to 72% and included metabolites in most major human metabolic pathways and chemical classes. Detection and feature quality varied by analytical configuration.
Conclusions: Dual chromatography HRM with positive and negative electrospray ionization provides an effective generalized method for metabolic assessment of military personnel.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

