MicroRNAs 29b and 181a down-regulate the expression of the norepinephrine transporter and glucocorticoid receptors in PC12 cells
- PMID: 27501468
- PMCID: PMC5056848
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.13761
MicroRNAs 29b and 181a down-regulate the expression of the norepinephrine transporter and glucocorticoid receptors in PC12 cells
Abstract
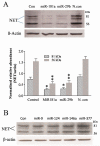
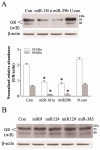
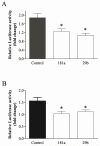
MicroRNAs are short non-coding RNAs that provide global regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Such regulation has been found to play a role in stress-induced epigenetic responses in the brain. The norepinephrine transporter (NET) and glucocorticoid receptors are closely related to the homeostatic integration and regulation after stress. Our previous studies demonstrated that NET mRNA and protein levels in rats are regulated by chronic stress and by administration of corticosterone, which is mediated through glucocorticoid receptors. Whether miRNAs are intermediaries in the regulation of these proteins remains to be elucidated. This study was undertaken to determine possible regulatory effects of miRNAs on the expression of NET and glucocorticoid receptors in the noradrenergic neuronal cell line. Using computational target prediction, we identified several candidate miRNAs potentially targeting NET and glucocorticoid receptors. Western blot results showed that over-expression of miR-181a and miR-29b significantly repressed protein levels of NET, which is accompanied by a reduced [3 H] norepinephrine uptake, and glucocorticoid receptors in PC12 cells. Luciferase reporter assays verified that both miR-181a and miR-29b bind the 3'UTR of mRNA of NET and glucocorticoid receptors. Furthermore, exposure of PC12 cells to corticosterone markedly reduced the endogenous levels of miR-29b, which was not reversed by the application of glucocorticoid receptor antagonist mifepristone. These observations indicate that miR-181a and miR-29b can function as the negative regulators of NET and glucocorticoid receptor translation in vitro. This regulatory effect may be related to stress-induced up-regulation of the noradrenergic phenotype, a phenomenon observed in stress models and depressive patients. This study demonstrated that miR-29b and miR-181a, two short non-coding RNAs that provide global regulation of gene expression, markedly repressed protein levels of norepinephrine (NE) transporter and glucocorticoid receptor (GR), as well as NE uptake by binding the 3'UTR of their mRNAs in PC12 cells. Also, exposure of cells to corticosterone significantly reduced miR-29b levels through a GR-independent way.
Keywords: PC12 cells; gene regulation; glucocorticoid receptor; microRNA; norepinephrine transporter; stress.
© 2016 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures


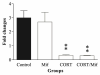
Similar articles
-
microRNA-181a is involved in insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated regulation of the transcription factor CREB1.J Neurochem. 2013 Sep;126(6):771-80. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12370. Epub 2013 Aug 6. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23865718
-
MicroRNA 18 and 124a down-regulate the glucocorticoid receptor: implications for glucocorticoid responsiveness in the brain.Endocrinology. 2009 May;150(5):2220-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1335. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19131573
-
Corticosterone up-regulates expression and function of norepinephrine transporter in SK-N-BE(2)C cells.J Neurochem. 2010 Apr;113(1):105-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06587.x. Epub 2010 Jan 13. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20070865 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-34 and MiR-200: Regulator of Cell Fate Plasticity and Neural Development.Neuromolecular Med. 2019 Jun;21(2):97-109. doi: 10.1007/s12017-019-08535-9. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Neuromolecular Med. 2019. PMID: 30963386 Review.
-
The role of miR-29b in cancer: regulation, function, and signaling.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Mar 3;8:539-48. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S75899. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 25767398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ligand-Dependent Downregulation of Guanylyl Cyclase/Natriuretic Peptide Receptor-A: Role of miR-128 and miR-195.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 2;23(21):13381. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113381. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362173 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Ethanol Challenge Differentially Regulates Expression of Growth Factors and miRNA Expression Profile of Whole Tissue of the Dorsal Hippocampus.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 30;16:884197. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.884197. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35706690 Free PMC article.
-
A New Insight into the Roles of MiRNAs in Metabolic Syndrome.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Dec 17;2018:7372636. doi: 10.1155/2018/7372636. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30648107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin A supplementation prevents the bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jan 22;100(3):e23101. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023101. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33545924 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors Phox2a/2b Upregulate Expression of Noradrenergic and Dopaminergic Phenotypes in Aged Rat Brains.Neurotox Res. 2020 Oct;38(3):793-807. doi: 10.1007/s12640-020-00250-9. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 32617854 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

