Preclinical anaylses of [18F]cEFQ as a PET tracer for imaging metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 (mGluR1)
- PMID: 27501957
- PMCID: PMC5464717
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X16663948
Preclinical anaylses of [18F]cEFQ as a PET tracer for imaging metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 (mGluR1)
Abstract
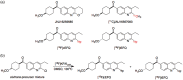
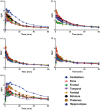
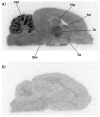
Metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 (mGluR1) is related with various neurological and psychiatric diseases, such as anxiety, depression, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and neuropathic pain. Hence, mGluR1 is an important target for drug development and imaging. We synthesized [18F]cEFQ (3-ethyl-2-[18F]fluoroquinolin-6-yl cis-(4-methoxycyclohexyl)methanone) as a PET tracer for selective mGluR1 imaging and evaluated its properties in rodents. A chloroquinoline precursor was labeled by a nucleophilic substitution reaction, and the resulting [18F]cEFQ was obtained with high radiochemical purity (>99%) and specific activity (63-246 GBq/µmol). The log D value was 3.24, and the initial brain uptake at 10 min was over 4% of injected dose per gram in BALB/c mice. According to PET/CT and autoradiography in SD rats, [18F]cEFQ showed wide distribution in the whole brain and the highest uptake in the cerebellum. Pre-treatment with unlabeled cEFQ or the mGluR1-specific antagonist JNJ16259685 blocked the uptake of [18F]cEFQ. However, the uptake was not blocked by pre-treatment with the mGluR5-specific antagonist ABP688. The trans isomer [18F]tEFQ did not show high uptake in the mGluR1-rich region. [18F]cEFQ was straightforwardly prepared using a chloro-derivative precursor. Its feasibility as a specific and selective PET agent for imaging mGluR1 was proved by in vitro and in vivo experiments using rodents.
Keywords: Autoradiography; [18F]cEFQ; metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1 (mGluR1); positron emission tomography (PET).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis and evaluation of novel radioligands for positron emission tomography imaging of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1 (mGluR1) in rodent brain.J Med Chem. 2012 Mar 8;55(5):2342-52. doi: 10.1021/jm201590g. Epub 2012 Feb 24. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22316010
-
Synthesis and evaluation of 6-[1-(2-[(18)F]fluoro-3-pyridyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl]quinoline for positron emission tomography imaging of the metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 in brain.Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Jan 1;19(1):102-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.11.048. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21172734
-
Radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation of 11C-ABP688 as a probe for imaging the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5.J Nucl Med. 2006 Apr;47(4):698-705. J Nucl Med. 2006. PMID: 16595505
-
In vivo imaging of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1) with positron emission tomography: recent advance and perspective.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(1):113-23. doi: 10.2174/09298673113209990217. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 23992339 Review.
-
(3-Ethyl-2-[11C]methyl-6-quinolinyl)(cis-4-methoxycyclohexyl)methanone.2012 Nov 15 [updated 2013 Mar 14]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 Nov 15 [updated 2013 Mar 14]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23534081 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
18 F-fluorodeoxy-glucose positron emission tomography pattern and prognostic predictors in patients with anti-GABAB receptor encephalitis.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Feb;28(2):269-278. doi: 10.1111/cns.13767. Epub 2021 Nov 26. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 34837479 Free PMC article.
-
KSNM60: The History of Radiopharmaceutical Sciences in Korea.Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Jun;56(3):114-126. doi: 10.1007/s13139-022-00744-8. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35607629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Molecular Imaging of Glutamate Receptors.Molecules. 2020 Oct 16;25(20):4749. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204749. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33081223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Monaghan DT, Bridges RJ, Cotman CW. The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 1989; 29: 365–402. - PubMed
-
- Hollmann M, Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Ann Rev Neurosci 1994; 17: 31–108. - PubMed
-
- Schoepp DD. Unveiling the functions of presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors in the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Therapeut 2001; 299: 12–20. - PubMed
-
- Lavreysen H, Pereira SN, Leysen JE, et al. Metabotropic glutamate 1 receptor distribution and occupancy in the rat brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study using [3H]R214127. Neuropharmacology 2004; 46: 609–619. - PubMed
-
- Steckler T, Lavreysen H, Oliveira AM, et al. Effects of mGlu1 receptor blockade on anxiety-related behaviour in the rat lick suppression test. Psychopharmacology 2005; 179: 198–206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

