Template-free Synthesis of One-dimensional Cobalt Nanostructures by Hydrazine Reduction Route
- PMID: 27502680
- PMCID: PMC3212205
- DOI: 10.1007/s11671-010-9807-7
Template-free Synthesis of One-dimensional Cobalt Nanostructures by Hydrazine Reduction Route
Abstract
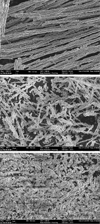
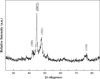
One-dimensional cobalt nanostructures with large aspect ratio up to 450 have been prepared via a template-free hydrazine reduction route under external magnetic field assistance. The morphology and properties of cobalt nanostructures were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometer, and vibrating sample magnetometer. The roles of the reaction conditions such as temperature, concentration, and pH value on morphology and magnetic properties of fabricated Co nanostructures were investigated. This work presents a simple, low-cost, environment-friendly, and large-scale production approach to fabricate one-dimensional magnetic Co materials. The resulting materials may have potential applications in nanodevice, catalytic agent, and magnetic recording.
Keywords: Cobalt nanowires; Hydration hydrazine reduction; Magnetic field assistance.
Figures



References
-
- Zeng H, Skomski R, Menon L, Liu Y, Bandyopadhyay S, Sellmyer D. Phys Rev B. 2002. p. 134426. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

