Widespread transneuronal propagation of α-synucleinopathy triggered in olfactory bulb mimics prodromal Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 27503075
- PMCID: PMC4995088
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20160368
Widespread transneuronal propagation of α-synucleinopathy triggered in olfactory bulb mimics prodromal Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by the progressive appearance of intraneuronal Lewy aggregates, which are primarily composed of misfolded α-synuclein (α-syn). The aggregates are believed to propagate via neural pathways following a stereotypical pattern, starting in the olfactory bulb (OB) and gut. We hypothesized that injection of fibrillar α-syn into the OB of wild-type mice would recreate the sequential progression of Lewy-like pathology, while triggering olfactory deficits. We demonstrate that injected α-syn fibrils recruit endogenous α-syn into pathological aggregates that spread transneuronally over several months, initially in the olfactory network and later in distant brain regions. The seeded inclusions contain posttranslationally modified α-syn that is Thioflavin S positive, indicative of amyloid fibrils. The spreading α-syn pathology induces progressive and specific olfactory deficits. Thus, we demonstrate that propagating α-syn pathology triggered in the OB is functionally detrimental. Collectively, we have created a mouse model of prodromal PD.
© 2016 Rey et al.
Figures
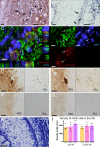



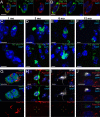

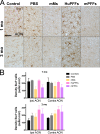
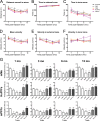

Comment in
-
Mechanisms for cell-to-cell propagation no longer lag behind.Mov Disord. 2016 Dec;31(12):1798-1799. doi: 10.1002/mds.26879. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Mov Disord. 2016. PMID: 27873365 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beach T.G., Adler C.H., Lue L., Sue L.I., Bachalakuri J., Henry-Watson J., Sasse J., Boyer S., Shirohi S., Brooks R., et al. Arizona Parkinson’s Disease Consortium . 2009. Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol. 117:613–634. 10.1007/s00401-009-0538-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

