A Nanoscale Interface Promoting Molecular and Functional Differentiation of Neural Cells
- PMID: 27503424
- PMCID: PMC4977496
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31226
A Nanoscale Interface Promoting Molecular and Functional Differentiation of Neural Cells
Abstract
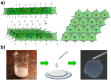
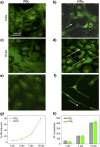
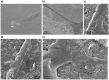
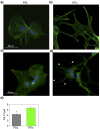
Potassium channels and aquaporins expressed by astrocytes are key players in the maintenance of cerebral homeostasis and in brain pathophysiologies. One major challenge in the study of astrocyte membrane channels in vitro, is that their expression pattern does not resemble the one observed in vivo. Nanostructured interfaces represent a significant resource to control the cellular behaviour and functionalities at micro and nanoscale as well as to generate novel and more reliable models to study astrocytes in vitro. However, the potential of nanotechnologies in the manipulation of astrocytes ion channels and aquaporins has never been previously reported. Hydrotalcite-like compounds (HTlc) are layered materials with increasing potential as biocompatible nanoscale interface. Here, we evaluate the effect of the interaction of HTlc nanoparticles films with primary rat neocortical astrocytes. We show that HTlc films are biocompatible and do not promote gliotic reaction, while favouring astrocytes differentiation by induction of F-actin fibre alignment and vinculin polarization. Western Blot, Immunofluorescence and patch-clamp revealed that differentiation was accompanied by molecular and functional up-regulation of both inward rectifying potassium channel Kir 4.1 and aquaporin 4, AQP4. The reported results pave the way to engineering novel in vitro models to study astrocytes in a in vivo like condition.
Figures




References
-
- Nedergaard M., Ransom B. & Goldman S. A. New roles for astrocytes: redefining the functional architecture of the brain. Trends Neurosci. 26, 523–530 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Benfenati V. & Ferroni S. Water transport between CNS compartments: functional and molecular interactions between aquaporins and ion channels. Neuroscience 168, 926–940 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Benfenati V. & Ferroni S. In Microdynamics of Water and Ion Homeostasis in the Brain: Role of Aquaporins and Ion Channels of Astroglial Cells; in Homeostatic control of brain function ; (eds Boison D. & Masino S. A.); First Edition, Oxford University Press (2015); “in press”.
-
- Kimelberg H. K. Astrocytic swelling in cerebral ischemia as a possible cause of injury and target for therapy. Glia 50, 389–397 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

