Crystallographic snapshots of sulfur insertion by lipoyl synthase
- PMID: 27506792
- PMCID: PMC5003258
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1602486113
Crystallographic snapshots of sulfur insertion by lipoyl synthase
Abstract
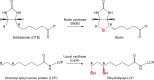
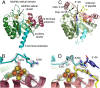
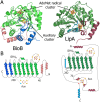
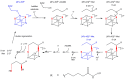
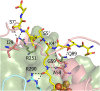
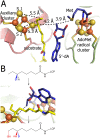
Lipoyl synthase (LipA) catalyzes the insertion of two sulfur atoms at the unactivated C6 and C8 positions of a protein-bound octanoyl chain to produce the lipoyl cofactor. To activate its substrate for sulfur insertion, LipA uses a [4Fe-4S] cluster and S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) radical chemistry; the remainder of the reaction mechanism, especially the source of the sulfur, has been less clear. One controversial proposal involves the removal of sulfur from a second (auxiliary) [4Fe-4S] cluster on the enzyme, resulting in destruction of the cluster during each round of catalysis. Here, we present two high-resolution crystal structures of LipA from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: one in its resting state and one at an intermediate state during turnover. In the resting state, an auxiliary [4Fe-4S] cluster has an unusual serine ligation to one of the irons. After reaction with an octanoyllysine-containing 8-mer peptide substrate and 1 eq AdoMet, conditions that allow for the first sulfur insertion but not the second insertion, the serine ligand dissociates from the cluster, the iron ion is lost, and a sulfur atom that is still part of the cluster becomes covalently attached to C6 of the octanoyl substrate. This intermediate structure provides a clear picture of iron-sulfur cluster destruction in action, supporting the role of the auxiliary cluster as the sulfur source in the LipA reaction and describing a radical strategy for sulfur incorporation into completely unactivated substrates.
Keywords: iron–sulfur cluster; lipoic acid; radical SAM enzyme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Miller JR, et al. Escherichia coli LipA is a lipoyl synthase: In vitro biosynthesis of lipoylated pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from octanoyl-acyl carrier protein. Biochemistry. 2000;39(49):15166–15178. - PubMed
-
- White RH. Stable isotope studies on the biosynthesis of lipoic acid in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980;19(1):15–19. - PubMed
-
- Douglas P, Kriek M, Bryant P, Roach PL. Lipoyl synthase inserts sulfur atoms into an octanoyl substrate in a stepwise manner. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2006;45(31):5197–5199. - PubMed
-
- Cicchillo RM, et al. Lipoyl synthase requires two equivalents of S-adenosyl-l-methionine to synthesize one equivalent of lipoic acid. Biochemistry. 2004;43(21):6378–6386. - PubMed
-
- Lieder KW, et al. S-Adenosylmethionine-dependent reduction of lysine 2,3-aminomutase and observation of the catalytically functional iron-sulfur centers by electron paramagnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1998;37(8):2578–2585. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

