Changes in Clinical Context for Kaposi's Sarcoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Among People With HIV Infection in the United States
- PMID: 27507879
- PMCID: PMC5024548
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.6999
Changes in Clinical Context for Kaposi's Sarcoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Among People With HIV Infection in the United States
Abstract
Purpose: The biology of HIV-associated cancers may differ depending on immunologic and virologic context during development. Therefore, an understanding of the burden of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) relative to antiretroviral therapy (ART), virologic suppression, and CD4 count is important.
Patients and methods: KS and NHL diagnoses during 1996 to 2011 were identified among patients with HIV infection in eight clinical cohorts in the United States. Among patients in routine HIV clinical care, the proportion of cases in categories of ART use, HIV RNA, and CD4 count at diagnosis were described across calendar time. Person-time and incidence rates were calculated for each category.
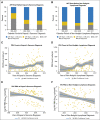
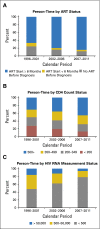
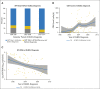
Results: We identified 466 patients with KS and 258 with NHL. In recent years, KS was more frequently diagnosed after ART initiation (55% in 1996 to 2001 v 76% in 2007 to 2011; P-trend = .02). The proportion of patients with NHL who received ART was higher but stable over time (83% overall; P-trend = .81). An increasing proportion of KS and NHL occurred at higher CD4 counts (P < .05 for KS and NHL) and with undetectable HIV RNA (P < .05 for KS and NHL). In recent years, more person-time was contributed by patients who received ART, had high CD4 counts and had undetectable HIV RNA, whereas incidence rates in these same categories remained stable or declined.
Conclusion: Over time, KS and NHL occurred at higher CD4 counts and lower HIV RNA values, and KS occurred more frequently after ART initiation. These changes were driven by an increasing proportion of patients with HIV who received effective ART, had higher CD4 counts, and had suppressed HIV RNA and not by increases in cancer risk within these subgroups. An improved understanding of HIV-associated cancer pathogenesis and outcomes in the context of successful ART is therefore important.
© 2016 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at www.jco.org. Author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Engels EA, Biggar RJ, Hall HI, et al. Cancer risk in people infected with human immunodeficiency virus in the United States. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Hjalgrim H, Engels EA. Infectious aetiology of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas: A review of the epidemiological evidence. J Intern Med. 2008;264:537–548. - PubMed
-
- Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM, Goedert JJ, et al. Trends in cancer risk among people with AIDS in the United States 1980-2002. AIDS. 2006;20:1645–1654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

