Complex Composite Odontoma
- PMID: 27507924
- PMCID: PMC4968180
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1066
Complex Composite Odontoma
Abstract
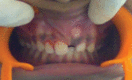
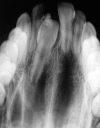
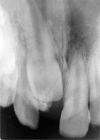
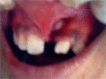
Odontomas are hamartomas composed of various dental tissues, i.e. enamel, dentin, cementum and sometimes pulp. They are slow-growing, benign tumors showing nonaggressive behavior. Most of the odontomes are asymptomatic with unknown etiology, although occasional signs and symptoms related to their presence do occur. Presented here is the case report of 10-year-old girl with impacted left central incisor.
Keywords: Complex; calcified; nonaggressive..
Figures



References
-
- Neville BW., Damm DD., Allen CM . Odontogenic cysts and tumors. In: Oral and maxillofacial pathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia (PA): WB Saunders; 2002. pp. 633–642.
-
- Mupparapu M, Singer SR, Rinaggio J. Complex odontoma of unusual size involving the maxillary sinus: Report of a case and review of CT and histopathologic features. Quintessence Int. 2004 Sep;35(8):641–645. - PubMed
-
- Cohen DM, Bhattacharyya I. Ameloblastic fibroma, ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, and odontoma. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2004 Aug;16(3):375–384. - PubMed
-
- Hitchin AD. The aetiology of the calcified composite odontomes. Br Dent J. 1971 Jun;130(11):475–482. - PubMed
-
- Kaugers GE, Miller ME, Abbey LM. Odontomas. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989 Feb;67(2):172–176. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
