Comparative growth of spotted fever group Rickettsia spp. strains in Vero cells
- PMID: 27508322
- PMCID: PMC4981112
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760160093
Comparative growth of spotted fever group Rickettsia spp. strains in Vero cells
Abstract
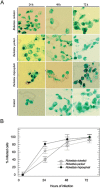
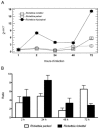
In Brazil, the spotted fever group (SFG) Rickettsia rickettsii and Rickettsia parkeri related species are the etiological agents of spotted fever rickettsiosis. However, the SFG, Rickettsia rhipicephali, that infects humans, has never been reported. The study of growth dynamics can be useful for understanding the infective and invasive capacity of these pathogens. Here, the growth rates of the Brazilian isolates R. rickettsii str. Taiaçu, R. parkeri str. At#24, and R. rhipicephali HJ#5, were evaluated in Vero cells by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. R. rhipicephali showed different kinetic growth compared to R. rickettsii and R. parkeri.
Figures
References
-
- Boldis V, Strus J, Kocianová E, Tusek-Znidaric M, Stefanidesová K, Schwarzová K, et al. Life cycle of Rickettsia slovaca in L929 cell line studied by quantitative real-time PCR and transmission electron microscopy. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009;293(1):102–106. - PubMed
-
- Burgdorfer W, Brinton LP, Krynski WL, Philip RN. In: Rickettsia rhipicephali, a new spotted fever group rickettsia from the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus; 2nd International Symposium on rickettsiae and rickettsial diseases; Bratislava: Public House of Slovak Academy of Sciences; 1978. pp. 307–316. Proceedings of the.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

