The in silico identification and characterization of a bread wheat/Triticum militinae introgression line
- PMID: 27510270
- PMCID: PMC5259550
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.12610
The in silico identification and characterization of a bread wheat/Triticum militinae introgression line
Abstract
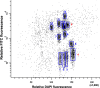
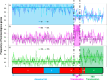
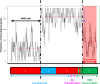
The capacity of the bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) genome to tolerate introgression from related genomes can be exploited for wheat improvement. A resistance to powdery mildew expressed by a derivative of the cross-bread wheat cv. Tähti × T. militinae (Tm) is known to be due to the incorporation of a Tm segment into the long arm of chromosome 4A. Here, a newly developed in silico method termed rearrangement identification and characterization (RICh) has been applied to characterize the introgression. A virtual gene order, assembled using the GenomeZipper approach, was obtained for the native copy of chromosome 4A; it incorporated 570 4A DArTseq markers to produce a zipper comprising 2132 loci. A comparison between the native and introgressed forms of the 4AL chromosome arm showed that the introgressed region is located at the distal part of the arm. The Tm segment, derived from chromosome 7G, harbours 131 homoeologs of the 357 genes present on the corresponding region of Chinese Spring 4AL. The estimated number of Tm genes transferred along with the disease resistance gene was 169. Characterizing the introgression's position, gene content and internal gene order should not only facilitate gene isolation, but may also be informative with respect to chromatin structure and behaviour studies.
Keywords: GenomeZipper; alien introgression; chromosome rearrangement; chromosome translocation; comparative analysis; linkage drag.
© 2016 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. A Kilian is head of Diversity Arrays Technology Pty Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Aflitos, S.A. , Sanchez‐Perez, G. , de Ridder, D. , Fransz, P. , Schranz, M.E. , de Jong, H. and Peters, S.A. (2015) Introgression browser: high‐throughput whole‐genome SNP visualization. Plant J. 82, 174–182. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S.F. , Gish, W. , Miller, W. , Myers, E.W. and Lipman, D.J. (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410. - PubMed
-
- Badaeva, E.D. , Budashkina, E.B. , Bilinskaya, E.N. and Pukhalskiy, V.A. (2010) Intergenomic chromosome substitutions in wheat interspecific hybrids and their use in the development of a genetic nomenclature of Triticum timopheevii chromosomes. Russian Journal of Genetics, 46, 769‐785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

