Calculating protein-ligand binding affinities with MMPBSA: Method and error analysis
- PMID: 27510546
- PMCID: PMC5018451
- DOI: 10.1002/jcc.24467
Calculating protein-ligand binding affinities with MMPBSA: Method and error analysis
Abstract
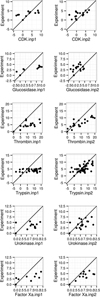
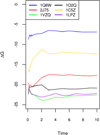
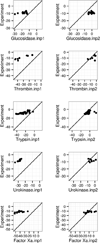
Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area (MMPBSA) methods have become widely adopted in estimating protein-ligand binding affinities due to their efficiency and high correlation with experiment. Here different computational alternatives were investigated to assess their impact to the agreement of MMPBSA calculations with experiment. Seven receptor families with both high-quality crystal structures and binding affinities were selected. First the performance of nonpolar solvation models was studied and it was found that the modern approach that separately models hydrophobic and dispersion interactions dramatically reduces RMSD's of computed relative binding affinities. The numerical setup of the Poisson-Boltzmann methods was analyzed next. The data shows that the impact of grid spacing to the quality of MMPBSA calculations is small: the numerical error at the grid spacing of 0.5 Å is already small enough to be negligible. The impact of different atomic radius sets and different molecular surface definitions was further analyzed and weak influences were found on the agreement with experiment. The influence of solute dielectric constant was also analyzed: a higher dielectric constant generally improves the overall agreement with experiment, especially for highly charged binding pockets. The data also showed that the converged simulations caused slight reduction in the agreement with experiment. Finally the direction of estimating absolute binding free energies was briefly explored. Upon correction of the binding-induced rearrangement free energy and the binding entropy lost, the errors in absolute binding affinities were also reduced dramatically when the modern nonpolar solvent model was used, although further developments were apparently necessary to further improve the MMPBSA methods. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: Poisson-Boltzmann implicit solvent models; molecular dynamics; nonpolar solvent models.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Statistical Analysis on the Performance of Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area versus Absolute Binding Free Energy Calculations: Bromodomains as a Case Study.J Chem Inf Model. 2017 Sep 25;57(9):2203-2221. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00347. Epub 2017 Aug 24. J Chem Inf Model. 2017. PMID: 28786670 Free PMC article.
-
A head-to-head comparison of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA in predicting binding affinities for the CB1 cannabinoid ligands.J Mol Model. 2024 Oct 31;30(11):390. doi: 10.1007/s00894-024-06189-4. J Mol Model. 2024. PMID: 39480515
-
Heterogeneous Dielectric Implicit Membrane Model for the Calculation of MMPBSA Binding Free Energies.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Jun 24;59(6):3041-3056. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00363. Epub 2019 Jun 13. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31145610 Free PMC article.
-
Implicit solvent methods for free energy estimation.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Feb 16;91:27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.08.064. Epub 2014 Aug 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25193298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments and Applications of the MMPBSA Method.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jan 10;4:87. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2017.00087. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29367919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A short HLA-DRA isoform binds the HLA-DR2 heterodimer on the outer domain of the peptide-binding site.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022 Apr 15;719:109156. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109156. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022. PMID: 35218721 Free PMC article.
-
Control Strategies of Plastic Biodegradation through Adjusting Additives Ratios Using In Silico Approaches Associated with Proportional Factorial Experimental Design.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 6;19(9):5670. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095670. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35565062 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Investigation on the p53-MDM2 Interaction Using the Potential of Mean Force Study.ACS Omega. 2020 Apr 10;5(15):8449-8462. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03372. eCollection 2020 Apr 21. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32337406 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic Solution: What Goes Right and Wrong with Continuum Solvation Modeling.J Phys Chem B. 2017 Dec 14;121(49):11169-11179. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b09616. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Phys Chem B. 2017. PMID: 29164898 Free PMC article.
-
In silico identification of promising PD-L1 inhibitors from selected indian medicinal plants for treatment of triple negative breast cancer.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 10;20(7):e0327475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327475. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40638667 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

