Coiled-coil destabilizing residues in the group A Streptococcus M1 protein are required for functional interaction
- PMID: 27512043
- PMCID: PMC5003295
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1606160113
Coiled-coil destabilizing residues in the group A Streptococcus M1 protein are required for functional interaction
Abstract
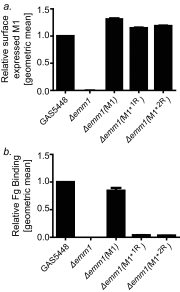
The sequences of M proteins, the major surface-associated virulence factors of the widespread bacterial pathogen group A Streptococcus, are antigenically variable but have in common a strong propensity to form coiled coils. Paradoxically, these sequences are also replete with coiled-coil destabilizing residues. These features are evident in the irregular coiled-coil structure and thermal instability of M proteins. We present an explanation for this paradox through studies of the B repeats of the medically important M1 protein. The B repeats are required for interaction of M1 with fibrinogen (Fg) and consequent proinflammatory activation. The B repeats sample multiple conformations, including intrinsically disordered, dissociated, as well as two alternate coiled-coil conformations: a Fg-nonbinding register 1 and a Fg-binding register 2. Stabilization of M1 in the Fg-nonbinding register 1 resulted in attenuation of Fg binding as expected, but counterintuitively, so did stabilization in the Fg-binding register 2. Strikingly, these register-stabilized M1 proteins gained the ability to bind Fg when they were destabilized by a chaotrope. These results indicate that M1 stability is antithetical to Fg interaction and that M1 conformational dynamics, as specified by destabilizing residues, are essential for interaction. A "capture-and-collapse" model of association accounts for these observations, in which M1 captures Fg through a dynamic conformation and then collapses into a register 2-coiled coil as a result of stabilization provided by binding energy. Our results support the general conclusion that destabilizing residues are evolutionarily conserved in M proteins to enable functional interactions necessary for pathogenesis.
Keywords: M protein; coiled coil; dynamics; fibrinogen; group A Streptococcus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coiled-coil structure of group A streptococcal M proteins. Different temperature stability of class A and C proteins by hydrophobic-nonhydrophobic amino acid substitutions at heptad positions a and d.Biochemistry. 1997 Apr 22;36(16):4987-94. doi: 10.1021/bi962971q. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9125521
-
Coiled-coil irregularities and instabilities in group A Streptococcus M1 are required for virulence.Science. 2008 Mar 7;319(5868):1405-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1154470. Science. 2008. PMID: 18323455 Free PMC article.
-
C repeats of the streptococcal M1 protein achieve the human serum albumin binding ability by flanking regions which stabilize the coiled-coil conformation.Biochemistry. 1997 Jul 1;36(26):8107-13. doi: 10.1021/bi962991s. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9201959
-
The nonideal coiled coil of M protein and its multifarious functions in pathogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;715:197-211. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-0940-9_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21557065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The streptococcal M protein: a highly versatile molecule.Trends Microbiol. 2010 Jun;18(6):275-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2010.02.007. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Trends Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20347595 Review.
Cited by
-
Solution structural model of the complex of the binding regions of human plasminogen with its M-protein receptor from Streptococcus pyogenes.J Struct Biol. 2019 Oct 1;208(1):18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2019.07.005. Epub 2019 Jul 10. J Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 31301349 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of C4BP-binding sequence patterns in Streptococcus pyogenes M and Enn proteins.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jul;300(7):107478. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107478. Epub 2024 Jun 13. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38879009 Free PMC article.
-
Sliding Mechanism at a Coiled-Coil Interface.Biophys J. 2019 Apr 2;116(7):1228-1238. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.02.026. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 30904175 Free PMC article.
-
Human LINE-1 retrotransposition requires a metastable coiled coil and a positively charged N-terminus in L1ORF1p.Elife. 2018 Mar 22;7:e34960. doi: 10.7554/eLife.34960. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29565245 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of measles virus gene expression by P protein coiled-coil properties.Sci Adv. 2019 May 8;5(5):eaaw3702. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw3702. eCollection 2019 May. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31086822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cole JN, Barnett TC, Nizet V, Walker MJ. Molecular insight into invasive group A streptococcal disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9(10):724–736. - PubMed
-
- Nilson BH, et al. Structure and stability of protein H and the M1 protein from Streptococcus pyogenes. Implications for other surface proteins of gram-positive bacteria. Biochemistry. 1995;34(41):13688–13698. - PubMed

