NF-κB and IRF1 Induce Endogenous Retrovirus K Expression via Interferon-Stimulated Response Elements in Its 5' Long Terminal Repeat
- PMID: 27512062
- PMCID: PMC5044829
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01503-16
NF-κB and IRF1 Induce Endogenous Retrovirus K Expression via Interferon-Stimulated Response Elements in Its 5' Long Terminal Repeat
Abstract
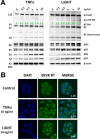
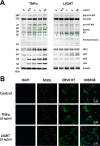
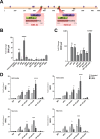
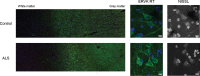
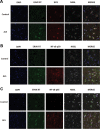
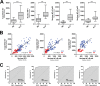
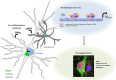
Thousands of endogenous retroviruses (ERV), viral fossils of ancient germ line infections, reside within the human genome. Evidence of ERV activity has been observed widely in both health and disease. While this is most often cited as a bystander effect of cell culture or disease states, it is unclear which signals control ERV transcription. Bioinformatic analysis suggests that the viral promoter of endogenous retrovirus K (ERVK) is responsive to inflammatory transcription factors. Here we show that one reason for ERVK upregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the presence of functional interferon-stimulated response elements (ISREs) in the viral promoter. Transcription factor overexpression assays revealed independent and synergistic upregulation of ERVK by interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) and NF-κB isoforms. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and LIGHT cytokine treatments of human astrocytes and neurons enhanced ERVK transcription and protein levels through IRF1 and NF-κB binding to the ISREs. We further show that in ALS brain tissue, neuronal ERVK reactivation is associated with the nuclear translocation of IRF1 and NF-κB isoforms p50 and p65. ERVK overexpression can cause motor neuron pathology in murine models. Our results implicate neuroinflammation as a key trigger of ERVK provirus reactivation in ALS. These molecular mechanisms may also extend to the pathobiology of other ERVK-associated inflammatory diseases, such as cancers, HIV infection, rheumatoid arthritis, and schizophrenia.
Importance: It has been well established that inflammatory signaling pathways in ALS converge at NF-κB to promote neuronal damage. Our findings suggest that inflammation-driven IRF1 and NF-κB activity promotes ERVK reactivation in neurons of the motor cortex in ALS. Thus, quenching ERVK activity through antiretroviral or immunomodulatory regimens may hinder virus-mediated neuropathology and improve the symptoms of ALS or other ERVK-associated diseases.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferons inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation via interferon regulatory factor-1 binding competition with NF-kappa B.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 20;277(38):35766-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202959200. Epub 2002 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12105194
-
TDP-43 regulates endogenous retrovirus-K viral protein accumulation.Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Oct;94:226-36. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.06.017. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Neurobiol Dis. 2016. PMID: 27370226
-
A tumor necrosis factor-α-responsive cryptic promoter drives overexpression of the human endogenous retrovirus ERVK-7.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):108568. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108568. Epub 2025 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40316021 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous retrovirus-K promoter: a landing strip for inflammatory transcription factors?Retrovirology. 2013 Feb 9;10:16. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-16. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 23394165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Human Endogenous Retroviruses and Endogenous Virus-Like Elements in Cancer Development and Innate Immunity.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 24;13(12):1706. doi: 10.3390/biom13121706. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Endogenous Retrovirus as Therapeutic Targets in Neurologic Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 May 24;14(6):495. doi: 10.3390/ph14060495. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transactive Response DNA-Binding Protein (TARDBP/TDP-43) Regulates Cell Permissivity to HIV-1 Infection by Acting on HDAC6.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 31;23(11):6180. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116180. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682862 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Immunity and Endogenous Retroelements in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Treatment Strategies.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Apr 9;25(1):85. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01583-4. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40205241 Review.
-
Retrotransposon: an insight into neurological disorders from perspectives of neurodevelopment and aging.Transl Neurodegener. 2025 Mar 25;14(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s40035-025-00471-y. Transl Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40128823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Freimanis G, Hooley P, Ejtehadi HD, Ali HA, Veitch A, Rylance PB, Alawi A, Axford J, Nevill A, Murray PG, Nelson PN. 2010. A role for human endogenous retrovirus-K (HML-2) in rheumatoid arthritis: investigating mechanisms of pathogenesis. Clin Exp Immunol 160:340–347. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04110.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

