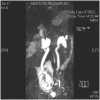
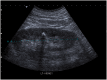
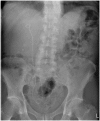
Renal stones in pregnancy
- PMID: 27512433
- PMCID: PMC4934980
- DOI: 10.1177/1753495X14538422
Renal stones in pregnancy
Abstract
Diagnosis and treatment of renal stones during pregnancy is a complex problem. Risks to the fetus from ionising radiation and interventional procedures need to be balanced with optimising clinical care for the mother. Management of such patients requires a clear understanding of available options, with a multidisciplinary team approach. In this review, we discuss the role of different diagnostic tests including ultrasound, magnetic resonance urography, and computerized tomography. We also provide an update on recent developments in the treatment of renal stones during pregnancy. Expectant management remains first-line treatment. Where definitive treatment of the stone is required, new evidence suggests that ureteroscopic stone removal may be equally safe, and possibly better than traditional temporising procedures.
Keywords: Renal stones; nephrolithiasis; pregnancy; urolithiasis.
Figures
References
-
- Marchant DJ. Effects of pregnancy and progestational agents on the urinary tract. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1972; 112: 487–501. - PubMed
-
- Rasmussen PE, Neilson FR. Hydronephrosis during pregnancy: A literature survey. Eur J Obstet Gynecology Reprod Biol 1988; 27: 249–259. - PubMed
-
- Peake SL, Roxburgh HB, Langlois SL. Ultrasonic assessment of hydronephrosis of pregnancy. Radiology 1983; 146: 167–170. - PubMed
-
- Nelson-Piercy Handbook of obstetric medicine, 4th ed London: Informa healthcare, 2010, pp. 176.
-
- Roberts JA. Hydronephrosis of pregnancy. Urology 1976; 8: 1–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources