Higher Ammonium Transamination Capacity Can Alleviate Glutamate Inhibition on Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Root Growth under High Ammonium Stress
- PMID: 27512992
- PMCID: PMC4981388
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160997
Higher Ammonium Transamination Capacity Can Alleviate Glutamate Inhibition on Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Root Growth under High Ammonium Stress
Abstract
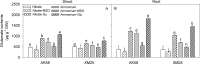
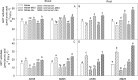
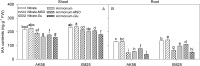
Most of the studies about NH4+ stress mechanism simply address the effects of free NH4+, failing to recognize the changed nitrogen assimilation products. The objective of this study was to elucidate the effects of glutamate on root growth under high ammonium (NH4+) conditions in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Hydroponic experiments were conducted using two wheat cultivars, AK58 (NH4+-sensitive) and Xumai25 (NH4+-tolerant) with either 5 mM NH4+ nitrogen (AN) as stress treatment or 5 mM nitrate (NO3-) nitrogen as control. To evaluate the effects of NH4+-assimilation products on plant growth, 1 μM L-methionine sulfoximine (MSO) (an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase (GS)) and 1 mM glutamates (a primary N assimilation product) were added to the solutions, respectively. The AN significantly reduced plant biomass, total root length, surface area and root volume in both cultivars, but less effect was observed in Xumai25. The inhibition effects were alleviated by the application of MSO but strengthened by the application of glutamate. The AN increased the activities of GS, glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) in both cultivars, resulting in higher glutamate contents. However, its contents were decreased by the application of MSO. Compared to AK58, Xumai25 showed lower glutamate contents due to its higher activities of glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) and glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (GPT). With the indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) contents decreasing in roots, the ratio of shoot to root in IAA was increased, and further increased by the application of glutamate, and reduced by the application of MSO, but the ratio was lower in Xumai25. Meanwhile, the total soluble sugar contents and its root to shoot ratio also showed similar trends. These results indicate that the NH4+-tolerant cultivar has a greater transamination ability to prevent glutamate over-accumulation to maintain higher IAA transport ability, and consequently promoted soluble sugar transport to roots, further maintaining root growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adaptation to rhizosphere acidification is a necessary prerequisite for wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedling resistance to ammonium stress.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016 Nov;108:447-455. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.08.011. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27569412
-
Nickel-induced changes in nitrogen metabolism in wheat shoots.J Plant Physiol. 2009 Jul 1;166(10):1034-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2008.12.004. Epub 2009 Jan 29. J Plant Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19185388
-
Molybdenum-Induced Effects on Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes and Elemental Profile of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Under Different Nitrogen Sources.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 20;20(12):3009. doi: 10.3390/ijms20123009. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31226753 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Important Enzymes Involved in Nitrogen Assimilation of Plants.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2057:1-13. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9790-9_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31595465 Review.
-
Alpha-ketoglutarate, a key molecule involved in nitrogen circulation in both animals and plants, in the context of human gut microbiota and protein metabolism.Adv Med Sci. 2022 Mar;67(1):142-147. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2022.02.004. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Adv Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35245838 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated physiological and weighted gene co-expression network analysis reveals the hub genes engaged in nitrate-regulated alleviation of ammonium toxicity at the seedling stage in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 17;13:1012966. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1012966. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36466221 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen fertilizer affects the cooking quality and starch properties of proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.).Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Nov 3;12(1):602-614. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3789. eCollection 2024 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38268879 Free PMC article.
-
Isotopic labelling reveals the efficient adaptation of wheat root TCA cycle flux modes to match carbon demand under ammonium nutrition.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 20;9(1):8925. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45393-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31222161 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen Regulating the Expression and Localization of Four Glutamine Synthetase Isoforms in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6299. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176299. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32878133 Free PMC article.
-
Higher Atmospheric CO2 Levels Favor C3 Plants Over C4 Plants in Utilizing Ammonium as a Nitrogen Source.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Dec 2;11:537443. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.537443. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33343587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen G, Guo S, Kronzucker HJ, Shi W (2013) Nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) in rice links to NH4+ toxicity and futile NH4+ cycling in roots. Plant and Soil: 1–13.
-
- Shi Z, Li D, Jing Q, Cai J, Jiang D, Cao W, et al. (2012) Effects of nitrogen applications on soil nitrogen balance and nitrogen utilization of winter wheat in a rice-wheat rotation. Field Crops Research 127: 241–247.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

