Understanding the Pathogenicity of Burkholderia contaminans, an Emerging Pathogen in Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 27512997
- PMCID: PMC4981469
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160975
Understanding the Pathogenicity of Burkholderia contaminans, an Emerging Pathogen in Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
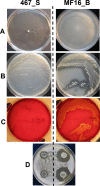
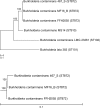
Several bacterial species from the Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc) are feared opportunistic pathogens that lead to debilitating lung infections with a high risk of developing fatal septicemia in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. However, the pathogenic potential of other Bcc species is yet unknown. To elucidate clinical relevance of Burkholderia contaminans, a species frequently isolated from CF respiratory samples in Ibero-American countries, we aimed to identify its key virulence factors possibly linked with an unfavorable clinical outcome. We performed a genome-wide comparative analysis of two isolates of B. contaminans ST872 from sputum and blood culture of a female CF patient in Argentina. RNA-seq data showed significant changes in expression for quorum sensing-regulated virulence factors and motility and chemotaxis. Furthermore, we detected expression changes in a recently described low-oxygen-activated (lxa) locus which encodes stress-related proteins, and for two clusters responsible for the biosynthesis of antifungal and hemolytic compounds pyrrolnitrin and occidiofungin. Based on phenotypic assays that confirmed changes in motility and in proteolytic, hemolytic and antifungal activities, we were able to distinguish two phenotypes of B. contaminans that coexisted in the host and entered her bloodstream. Whole genome sequencing revealed that the sputum and bloodstream isolates (each representing a distinct phenotype) differed by over 1,400 mutations as a result of a mismatch repair-deficient hypermutable state of the sputum isolate. The inferred lack of purifying selection against nonsynonymous mutations and the high rate of pseudogenization in the derived isolate indicated limited evolutionary pressure during evolution in the nutrient-rich, stable CF sputum environment. The present study is the first to examine the genomic and transcriptomic differences between longitudinal isolates of B. contaminans. Detected activity of a number of putative virulence factors implies a genuine pathogenic nature of this novel Bcc species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

