Quercetin and Cisplatin combined treatment altered cell cycle and mitogen activated protein kinase expressions in malignant mesotelioma cells
- PMID: 27514524
- PMCID: PMC4982421
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1267-x
Quercetin and Cisplatin combined treatment altered cell cycle and mitogen activated protein kinase expressions in malignant mesotelioma cells
Abstract
Background: Malignant mesothelioma is a locally aggressive and highly lethal neoplasm of pleural, peritoneal and pericardial mesothelial cells without successful therapy. Previously, we reported that Quercetin in combination with Cisplatin inhibits cell proliferation and activates caspase-9 and -3 enzymes in different malignant mesothelioma cell lines. Moreover, Quercetin + Cisplatin lead to accumulation of both SPC111 and SPC212 cell lines in S phase.
Methods: In present work, 84 genes involved in cell growth and proliferation have analysed by using RT(2)-PCR array system and protein profile of mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) family proteins investigated by western blots.
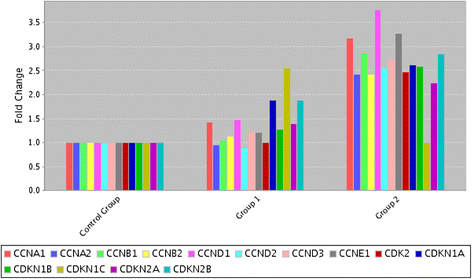
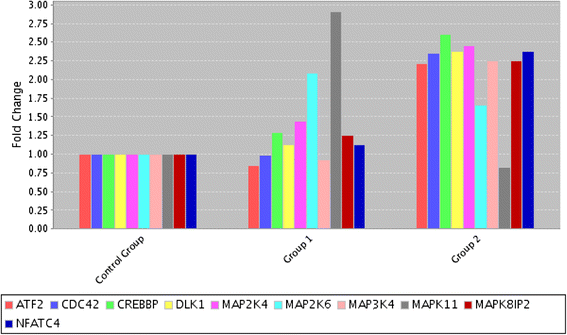
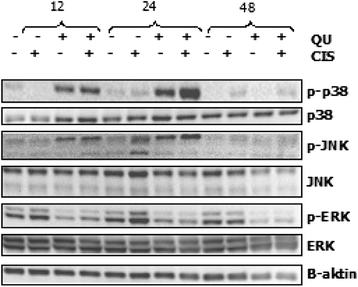
Results: Our results showed that Quercetin and Quercetin + Cisplatin modulated gene expression of cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases and cyclin dependent kinases inhibitors. In addition genes involved in JNK, p38 and MAPK/ERK pathways were up regulated. Moreover, while p38 and JNK phosphorylations were increased, ERK phosphorylations were decreased after using Quercetin + Cisplatin.
Conclusion: This research has clarified our previous results and detailed mechanism of anti-carcinogenic potential of Quercetin alone and incombination with Cisplatin on malignant mesothelioma cells.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Cisplatin; JNK; MAPK; Mesothelioma; Quercetin; p38.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pharmacological targeting of p53 through RITA is an effective antitumoral strategy for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(4):652-65. doi: 10.4161/cc.27546. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24345738
-
Synergistic anti-tumor effect of bullfrog sialic acid-binding lectin and pemetrexed in malignant mesothelioma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(26):42466-42477. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17198. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28476017 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in inhibition of proliferation in human prostate carcinoma cells by raloxifene: an in vitro experiment].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Jan 22;88(4):271-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18361842 Chinese.
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by cisplatin and their role in cisplatin-resistance.Cancer Lett. 2007 Jun 18;251(1):1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2006.10.007. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Cancer Lett. 2007. PMID: 17125914 Review.
-
Regulation of microRNA using promising dietary phytochemicals: Possible preventive and treatment option of malignant mesothelioma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Oct;94:1197-1224. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.075. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28841784 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of a Polyphenolic Phytochemical Quercetin against Oxidative Dysfunctions in Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Apr 20;2023:7858718. doi: 10.1155/2023/7858718. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37123083 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Quercetin-Sensitized Cisplatin against N-Nitroso-NMethylurea Induced Testicular Carcinogenesis in Wistar Rats.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Jan 1;22(1):75-84. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.1.75. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 33507682 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of essential oil of Origanum onites and its major component carvacrol on the expression of toxicity pathway genes in HepG2 cells.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Jul 11;24(1):265. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04571-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 38992651 Free PMC article.
-
KMT2D deficiency enhances the anti-cancer activity of L48H37 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019 Aug 15;11(8):599-621. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i8.599. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31435462 Free PMC article.
-
Size-Dependent Biological Effects of Quercetin Nanocrystals.Molecules. 2019 Apr 11;24(7):1438. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071438. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30979064 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

