Validation and Comparison of Seven Mortality Prediction Models for Hospitalized Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
- PMID: 27514749
- PMCID: PMC4988343
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002912
Validation and Comparison of Seven Mortality Prediction Models for Hospitalized Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) inpatient mortality prediction models can help clinicians make treatment decisions and researchers conduct observational studies; however, published models have not been validated in external populations.
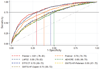
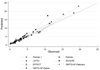
Methods and results: We compared the performance of 7 models that predict inpatient mortality in patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: 4 HF-specific mortality prediction models developed from 3 clinical databases (ADHERE [Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry], EFFECT study [Enhanced Feedback for Effective Cardiac Treatment], and GWTG-HF registry [Get With the Guidelines-Heart Failure]); 2 administrative HF mortality prediction models (Premier, Premier+); and a model that uses clinical data but is not specific for HF (Laboratory-Based Acute Physiology Score [LAPS2]). Using a multihospital, electronic health record-derived data set (HealthFacts [Cerner Corp], 2010-2012), we identified patients ≥18 years admitted with HF. Of 13 163 eligible patients, median age was 74 years; half were women; and 27% were black. In-hospital mortality was 4.3%. Model-predicted mortality ranges varied: Premier+ (0.8%-23.1%), LAPS2 (0.7%-19.0%), ADHERE (1.2%-17.4%), EFFECT (1.0%-12.8%), GWTG-Eapen (1.2%-13.8%), and GWTG-Peterson (1.1%-12.8%). The LAPS2 and Premier models outperformed the clinical models (C statistics: LAPS2 0.80 [95% confidence interval 0.78-0.82], Premier models 0.81 [95% confidence interval 0.79-0.83] and 0.76 [95% confidence interval 0.74-0.78], and clinical models 0.68 to 0.70).
Conclusions: Four clinically derived, inpatient, HF mortality models exhibited similar performance, with C statistics near 0.70. Three other models, 1 developed in electronic health record data and 2 developed in administrative data, also were predictive, with C statistics from 0.76 to 0.80. Because every model performed acceptably, the decision to use a given model should depend on practical concerns and intended use.
Keywords: heart failure; hospitalization; inpatients; mortality prediction; treatment outcome.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Model Building as an Educational Hobby.Circ Heart Fail. 2016 Aug;9(8):e003457. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.116.003457. Circ Heart Fail. 2016. PMID: 27514752 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Ford E, Furie K, Gillespie C, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho PM, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott MM, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino M, Nichol G, Roger VL, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Roger VL, Stafford R, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong ND, Wylie-Rosett J. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:e46–e215. - PubMed
-
- Krumholz HM, Merrill AR, Schone EM, Schreiner GC, Chen J, Bradley EH, Wang Y, Wang Y, Lin Z, Straube BM, Rapp MT, Normand S-LT, Drye EE. Patterns of hospital performance in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure 30-day mortality and readmission. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2009;2:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Bernheim SM, Grady JN, Lin Z, Wang Y, Wang Y, Savage SV, Bhat KR, Ross JS, Desai MM, Merrill AR, Han LF, Rapp MT, Drye EE, Normand S-LT, Krumholz HM. National patterns of risk-standardized mortality and readmission for acute myocardial infarction and heart failure. Update on publicly reported outcomes measures based on the 2010 release. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2010;3:459–467. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fonarow GC, Adams KF, Abraham WT, Yancy CW, Boscardin WJ ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee, Study Group, and Investigators. Risk stratification for in-hospital mortality in acutely decompensated heart failure: classification and regression tree analysis. JAMA. 2005;293:572–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous