Autophagy in the liver: cell's cannibalism and beyond
- PMID: 27515049
- PMCID: PMC5007189
- DOI: 10.1007/s12272-016-0807-8
Autophagy in the liver: cell's cannibalism and beyond
Abstract
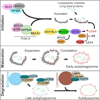
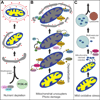
Chronic liver disease and its progression to liver failure are induced by various etiologies including viral infection, alcoholic and nonalcoholic hepatosteatosis. It is anticipated that the prevalence of fatty liver disease will continue to rise due to the growing incidence of obesity and metabolic disorder. Evidence is accumulating to indicate that the onset of fatty liver disease is causatively linked to mitochondrial dysfunction and abnormal lipid accumulation. Current treatment options for this disease are limited. Autophagy is an integral catabolic pathway that maintains cellular homeostasis both selectively and nonselectively. As mitophagy and lipophagy selectively remove dysfunctional mitochondria and excess lipids, respectively, stimulation of autophagy could have therapeutic potential to ameliorate liver function in steatotic patients. This review highlights our up-to-date knowledge on mechanistic roles of autophagy in the pathogenesis of fatty liver disease and its vulnerability to surgical stress, with an emphasis on mitophagy and lipophagy.
Keywords: Autophagy; Lipophagy; Liver; Mitophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors disclose no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aoun M, Fouret G, Michel F, Bonafos B, Ramos J, Cristol JP, Carbonneau MA, Coudray C, Feillet-Coudray C. Dietary fatty acids modulate liver mitochondrial cardiolipin content and its fatty acid composition in rats with non alcoholic fatty liver disease. J.Bioenerg.Biomembr. 2012;44:439–452. - PubMed
-
- Argo CK, Caldwell SH. Epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin.Liver Dis. 2009;13:511–531. - PubMed
-
- Bailey SM, Cunningham CC. Acute and chronic ethanol increases reactive oxygen species generation and decreases viability in fresh, isolated rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1998;28:1318–1326. - PubMed
-
- Bailey SM, Cunningham CC. Effect of dietary fat on chronic ethanol-induced oxidative stress in hepatocytes. Alcohol Clin.Exp.Res. 1999;23:1210–1218. - PubMed
-
- Baraona E, Pirola RC, Lieber CS. Acute and chronic effects of ethanol on intestinal lipid metabolism. Biochim.Biophys.Acta. 1975;388:19–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

