Exendin-4 enhances the differentiation of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-producing cells through activation of various β-cell markers
- PMID: 27515427
- PMCID: PMC4981957
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-016-0374-4
Exendin-4 enhances the differentiation of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-producing cells through activation of various β-cell markers
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a devastating metabolic disease. Generation of insulin-producing cells (IPCs) from stem cells, especially from Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSCs), has sparked much interest recently. Exendin-4 has several beneficial effects on MSCs and β cells. However, its effects on generation of IPCs from WJ-MSCs specifically have not been studied adequately. The purpose of this study was therefore to investigate how exendin-4 could affect the differentiation outcome of WJ-MSCs into IPCs, and to investigate the role played by exendin-4 in this differentiation process.
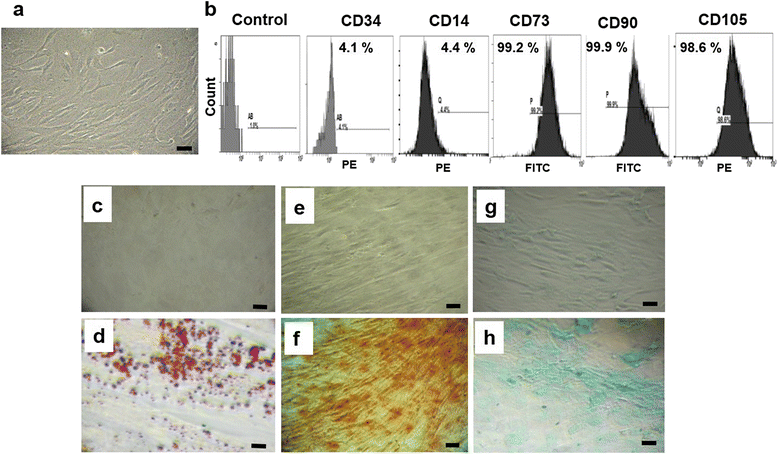
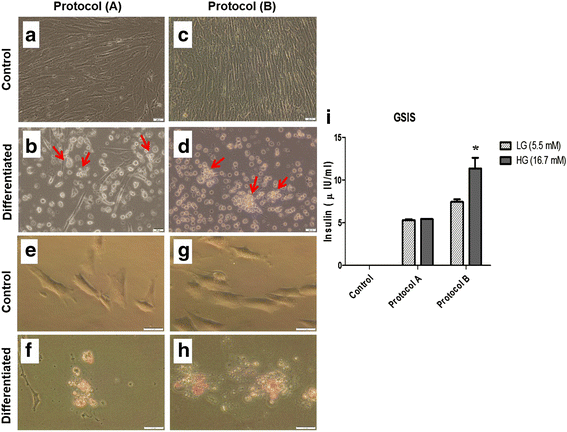
Methods: WJ-MSCs were isolated, characterized and then induced to differentiate into IPCs using two differentiation protocols: protocol A, without exendin-4; and protocol B, with exendin-4. Differentiated IPCs were assessed by the expression of various β-cell-related markers using quantitative RT-PCR, and functionally by measuring glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.
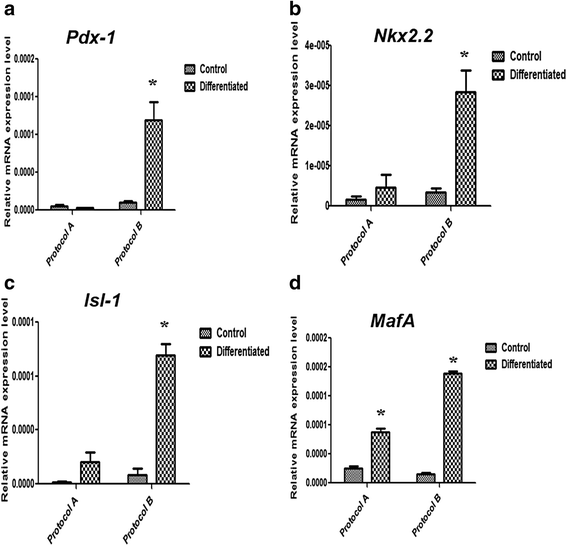
Results: The differentiation protocol B incorporating exendin-4 significantly boosted the expression levels of β-cell-related genes Pdx-1, Nkx2.2, Isl-1 and MafA. Moreover, IPCs generated by protocol B showed much better response to variable glucose concentrations as compared with those derived from protocol A, which totally lacked such response. Furthermore, exendin-4 alone induced early differentiation markers such as Pdx-1 and Nkx2.2 but not Isl-1, besides inducing late markers such as MafA. In addition, exendin-4 showed a synergistic effect with nicotinamide and β-mercaptoethanol in the induction of these markers.
Conclusions: Exendin-4 profoundly improves the differentiation outcome of WJ-MSCs into IPCs, possibly through the ability to induce the expression of β-cell markers.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Exendin-4; Insulin-producing cells; Mesenchymal stem cells; Wharton’s jelly.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Obestatin can potentially differentiate Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-producing cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Apr;372(1):91-98. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2725-6. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 29159483
-
Association of expression levels of pluripotency/stem cell markers with the differentiation outcome of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells into insulin producing cells.Biochimie. 2016 Aug;127:187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.05.019. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 27265786
-
Differentiation of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells into endometrial cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;8(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0700-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096715 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Wharton's Jelly and Amniotic Fluid.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016 Feb;31:30-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016. PMID: 26482184 Review.
-
Wharton's Jelly MSCs: Potential Weapon to Sharpen for Our Battle against DM.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Apr;31(4):271-273. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32035737 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Clopidogrel and Ticagrelor on Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation Potential: In Vitro Comparative Study.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 Feb 15;2024:2990670. doi: 10.1155/2024/2990670. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38390313 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Duct Cells Isolated From Canines Differentiate Into Beta-Like Pancreatic Islet Cells.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jan 5;8:771196. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.771196. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35071380 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1: a new potential regulator for mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complication.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 May 19;16(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04369-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40390070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in apoptotic pathways and expression of miR-134, miR-181, and miR-497 induced by Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of ischemic brain injury.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025 Apr 28;18:759-770. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.04.015. eCollection 2025 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40502966 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of diabetes mellitus on differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-producing cells.Biol Res. 2024 May 2;57(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00502-4. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38698488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IDF. International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 7th ed. 2015. http://www.diabetesatlas.org/resources/2015-atlas.html. Accessed 1 Apr 2016.
-
- Bruin JE, Rezania A, Kieffer TJ. Replacing and safeguarding pancreatic β cells for diabetes. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(316):316 ps323. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

