An anatomic study of the lateral patellofemoral ligament
- PMID: 27516002
- PMCID: PMC6197417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aott.2016.07.009
An anatomic study of the lateral patellofemoral ligament
Abstract
Objective: The lateral patellofemoral ligament (LPFL) is part of the lateral retinaculum cut during arthroscopic or open release. We investigated its anatomic and morphometric characteristics.
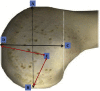
Materials and methods: We identified the LPFL insertion point on the condyle in vertical and sagittal planes in 32 adult cadaveric knees. We measured its length and width at the insertion point. We located the midpoint of this point and measured from it to the distal and posterior condylar ends. We measured anterior-posterior and proximal-distal lateral condylar lengths. We evaluated the insertion point shape on the lateral femoral condyle. Degree of relationship between variables was assessed using Pearson's correlation coefficient. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: The LPFL mean length was 23.2 mm, and mean width at the insertion point was 15.6 mm. Regarding its insertion into the lateral condyle, central insertions were more frequent (vertical plane: 53.1% central and sagittal plane: 75% central). A significant positive correlation was evident between the LPFL length and width at the insertion point (p = 0.05). Thus, the LPFL length was proportional to its width at the insertion point. A significant positive correlation was found between the anterior-posterior condylar length and width of the LPFL at the insertion point (p = 0.017). Therefore, greater anterior-posterior condylar length equates to a larger area of insertion on the condyle.
Conclusion: Greater width of the LPFL at the insertion point corresponds to greater LPFL and anterior-posterior lateral condylar lengths.
Keywords: Anatomic study; Lateral condyle of the femur; Lateral patellofemoral ligament.
Copyright © 2016 Turkish Association of Orthopaedics and Traumatology. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Andrikoula S., Tokis A., Vasiliadis H.S., Georgoulis A. The extensor mechanism of the knee joint: an anatomical study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:214–220. - PubMed
-
- Conlan T., Garth W.P., Lemons J.E. Evaluation of the medial soft-tissue restraints of the extensor mechanism of the knee. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1993;75:682–693. - PubMed
-
- Desio S.M., Burks R.T., Bachus K.N. Soft tissue restraints to lateral patellar translation in the human knee. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26:59–65. - PubMed
-
- Hautamaa P.V., Fithian D.C., Kaufman K.R., Daniel D.M., Pohlmeyer A.M. Medial soft tissue restraints in lateral patellar instability and repair. Clin Orthop. 1998;349:174–182. - PubMed
-
- Nomura E., Horiuchi Y., Kihara M. Medial patellofemoral ligament restraint in lateral patellar translation and reconstruction. Knee. 2000;7:121–127. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
