Targeting hepatic glucose metabolism in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 27516169
- PMCID: PMC5751421
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2016.151
Targeting hepatic glucose metabolism in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
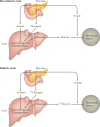
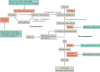
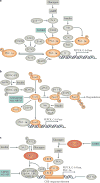
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by the dysregulation of glucose homeostasis, resulting in hyperglycaemia. Although current diabetes treatments have exhibited some success in lowering blood glucose levels, their effect is not always sustained and their use may be associated with undesirable side effects, such as hypoglycaemia. Novel antidiabetic drugs, which may be used in combination with existing therapies, are therefore needed. The potential of specifically targeting the liver to normalize blood glucose levels has not been fully exploited. Here, we review the molecular mechanisms controlling hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogen storage, and assess the prospect of therapeutically targeting associated pathways to treat type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Atlanta, ga: US Department of health and human services; 2014. National diabetes statistics report: estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States, 2014.
-
- Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world--a growing challenge. The New England journal of medicine. 2007;356:213–215. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes care. 1992;15:318–368. - PubMed
-
- Foretz M, Guigas B, Bertrand L, Pollak M, Viollet B. Metformin: from mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell metabolism. 2014;20:953–966. This work reviews the complexities surrounding the mechanism of action of metformin, the most widely used anti-diabetic drug. - PubMed
-
- Gribble FM, Reimann F. Sulphonylurea action revisited: the post-cloning era. Diabetologia. 2003;46:875–891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

