Efficacy and Safety of the Woven EndoBridge (WEB) Device for the Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27516237
- PMCID: PMC7963876
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A4900
Efficacy and Safety of the Woven EndoBridge (WEB) Device for the Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Intrasaccular flow diverters are increasingly being used in the treatment of wide-neck and bifurcation aneurysms. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of existing literature on the Woven EndoBridge device in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms.
Materials and methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed through October 1, 2015. We extracted information on baseline aneurysm and patient characteristics. Outcomes studied included immediate and midterm (>3 month) angiographic outcomes (complete occlusion as well as adequate occlusion, defined as complete occlusion or neck remnant), aneurysm retreatment, intraoperative rupture, perioperative morbidity and mortality, thromboembolic complications, and treatment failure. Meta-analysis was performed by using the random-effects model.
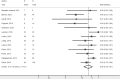
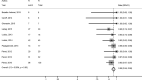
Results: Fifteen uncontrolled series were included in this analysis, including 565 patients with 588 aneurysms, of which 127 were ruptured. Initial complete and adequate occlusion rates were 27% (95% CI, 15%-39%) and 59% (95% CI, 39%-78%), respectively. Midterm complete and adequate occlusion rates after a median of 7 months were 39% (95% CI, 26%-52%) and 85% (95% CI, 78%-91%), respectively. Perioperative morbidity and mortality rates were 4% (95% CI, 1%-8%) and 1% (95% CI, 0%-2%), respectively. Midterm adequate occlusion rates for ruptured aneurysms were 85% (95% CI, 67%-98%), compared with 84% (95% CI, 72%-94%) for unruptured aneurysms (P = .89). Patients with ruptured aneurysm had similar rates of perioperative morbidity to patients with unruptured aneurysm (2%; 95% CI, 0%-26% versus 2%; 95% CI, 0%-6%, respectively; P = .35).
Conclusions: Early evidence derived from uncontrolled studies suggests that Woven EndoBridge treatment has a good safety profile and promising rates of adequate occlusion, especially given the complexity of aneurysms treated. Further prospective clinical trials are needed to confirm these results and better define the risks and benefits of use of the Woven EndoBridge device in treating wide-neck and wide-neck bifurcation aneurysms.
© 2016 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reply.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Jan;38(1):E8. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4987. Epub 2016 Oct 13. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 27737855 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
More Transparency Is Needed in the Reporting of Clinical Research Studies.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Jan;38(1):E6-E7. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4982. Epub 2016 Oct 13. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 27737856 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Moret J, Cognard C, Weill A, et al. . The “remodelling technique” in the treatment of wide neck intracranial aneurysms: angiographic results and clinical follow-up in 56 cases. Interv Neuroradiol 1997;3:21–35 - PubMed
-
- Mu SQ, Yang XJ, Li YX, et al. . Endovascular treatment of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms using of “remodeling technique” with the HyperForm balloon. Chin Med J (Engl) 2008;121:725–29 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical