Influence of Environmental Factors on Phage-Bacteria Interaction and on the Efficacy and Infectivity of Phage P100
- PMID: 27516757
- PMCID: PMC4964841
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01152
Influence of Environmental Factors on Phage-Bacteria Interaction and on the Efficacy and Infectivity of Phage P100
Abstract
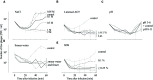
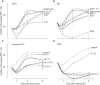
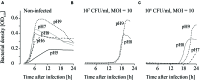
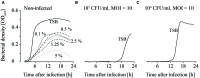
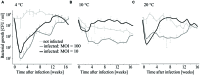
When using bacteriophages to control food-borne bacteria in food production plants and processed food, it is crucial to consider that environmental conditions influence their stability. These conditions can also affect the physiological state of bacteria and consequently host-virus interaction and the effectiveness of the phage ability to reduce bacteria numbers. In this study we investigated the stability, binding, and replication capability of phage P100 and its efficacy to control Listeria monocytogenes under conditions typically encountered in dairy plants. The influences of SDS, Lutensol AO 7, salt, smear water, and different temperatures were investigated. Results indicate that phage P100 is stable and able to bind to the host under most conditions tested. Replication was dependent upon the growth of L. monocytogenes and efficacy was higher when bacterial growth was reduced by certain environmental conditions. In long-term experiments at different temperatures phages were initially able to reduce bacteria up to seven log10 units after 2 weeks at 4°C. However, thereafter, re-growth and development of phage-resistant L. monocytogenes isolates were encountered.
Keywords: L. monocytogenes; ListexTM P100; bacteriophage P100; environmental influence; host–phage interaction; resistance.
Figures
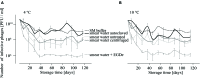

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

